Page 65 - AN-4-2
P. 65
Advanced Neurology Brain bioavailability of targeted protein degraders
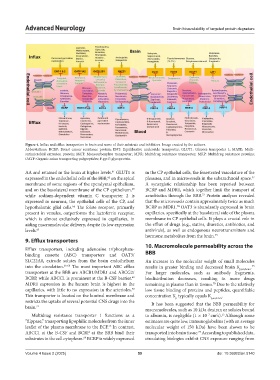
Figure 4. Influx and efflux transporters in brain and some of their substrate and inhibitors. Image created by the authors.
Abbreviations: BCRP: Breast cancer resistance protein; ENT: Equilibrative nucleoside transporter; GLUT1: Glucose transporter 1; MATE: Multi-
antimicrobial extrusion protein; MCT: Monocarboxylate transporter; MDR: Multidrug resistance transporter; MRP: Multidrug resistance proteins;
OATP: Organic anion transporting polypeptides; P-gp: P-glycoprotein.
AA and retained in the brain at higher levels. GLUT1 is in the CP epithelial cells, the fenestrated vasculature of the
61
expressed in the endothelial cells of the BBB, on the apical plexuses, and in microvessels in the subarachnoid space.
62
37
membrane of some regions of the ependymal epithelium, A synergistic relationship has been reported between
and on the basolateral membrane of the CP epithelium, BCRP and MDR1, which together limit the transport of
63
while sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 is xenobiotics through the BBB. Protein analyses revealed
73
expressed in neurons, the epithelial cells of the CP, and that the microvessels contain approximately twice as much
hypothalamic glial cells. The folate receptor, primarily BCRP as MDR1. OAT3 is abundantly expressed in brain
74
64
present in venules, outperforms the lactoferrin receptor, capillaries, specifically at the basolateral side of the plasma
which is almost exclusively expressed in capillaries, in membrane in CP epithelial cells. It plays a crucial role in
aiding macromolecular delivery, despite its low expression the efflux of drugs (e.g., statins, diuretics, antibiotics, and
levels. 65 antivirals), as well as endogenous neurotransmitters and
hormone metabolites from the brain. 43
9. Efflux transporters
10. Macromolecule permeability across the
Efflux transporters, including adenosine triphosphate-
binding cassette (ABC) transporters and OAT3/ BBB
SLC22A8, extrude solutes from the brain endothelium An increase in the molecular weight of small molecules
into the circulation. 66-68 The most important ABC efflux results in greater binding and decreased brain K p,uu,brain .
75
transporters at the BBB are ABCB1/MDR1 and ABCG2/ For larger molecules, such as antibody fragments,
BCRP, while ABCC1 is prominent at the B-CSF barrier. biodistribution decreases, resulting in more drugs
69
MDR1 expression in the human brain is highest in the remaining in plasma than in tissues. Due to the relatively
76
capillaries, with little to no expression in the arterioles. low tissue binding of proteins and peptides, quantifiable
70
This transporter is located on the luminal membrane and concentration K typically equals K p,uu,brain .
p
restricts the uptake of several potential CNS drugs into the It has been suggested that the BBB permeability for
brain. 71
macromolecules, such as 10 kDa dextran or solutes bound
Multidrug resistance transporter 1 functions as a to albumin, is negligible (1 × 10 cm s). Although some
13
/
−7
“flippase,” transporting lipophilic molecules from the inner estimates are quite low, immunoglobulins (with an average
leaflet of the plasma membrane to the ECF. In contrast, molecular weight of 150 kDa) have been shown to be
72
77
ABCC1 at the B-CSF and BCRP at the BBB bind their transported into brain tissue. According to published data,
substrates in the cell cytoplasm. BCRP is widely expressed circulating biologics exhibit CNS exposure ranging from
69
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 59 doi: 10.36922/an.5140