Page 69 - AN-4-2
P. 69
Advanced Neurology Brain bioavailability of targeted protein degraders
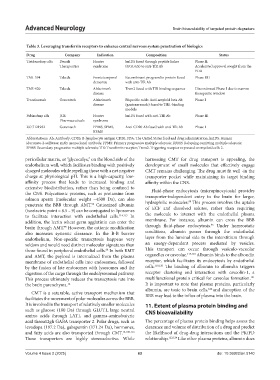
Table 3. Leveraging transferrin receptors to enhance central nervous system penetration of biologics
Drug Company Indication Composition Status
Tividenofusp alfa Denali Hunter huIDS fused through peptide linker Phase II;
Therapeutics syndrome (GGGGS) to anti-TfR Ab Accelerated approval sought from the
FDA
TAK-594 Takeda Frontotemporal Recombinant progranulin protein fused Phase I/II
dementia with anti-TfR Ab
TAK-920 Takeda Alzheimer’s Trem2 fused with TfR binding sequence Discontinued Phase I due to narrow
disease therapeutic window
Trontinemab Genentech Alzheimer’s Bispecific mAb: Anti-amyloid beta Ab Phase I
disease (gantenerumab) fused to TfR1-binding
module
Pabinafusp alfa JCR Hunter huIDS fused with anti-TfR Ab Phase III
Pharmaceuticals syndrome
RO 7121932 Genentech PPMS, SPMS, Anti-CD20 Ab fused with anti-TfR Ab Phase I
RRMS
Abbreviations: Ab: Antibody; CD20: B-lymphocyte antigen CD20; FDA: The United States food and drug administration; huIDS: Human
iduronate-2-sulfatase; mAb: monoclonal antibody, PPMS: Primary progressive multiple sclerosis; RRMS: Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis;
SPMS: Secondary progressive multiple sclerosis; TfR: Transferrin receptor; Trem2: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
pericellular matrix, or “glycocalyx,” on the blood side of the harnessing CMT for drug transport is appealing, the
endothelium wall, which facilitates binding with positively development of small molecules that effectively engage
charged molecules while repelling those with a net negative CMT remains challenging. The drug must fit well -in the
charge at physiological pH. This is a high-capacity, low- transporter pocket while maintaining its target binding
affinity process that leads to increased binding and affinity within the CNS.
extensive biodistribution, rather than being confined to
the CNS. Polycationic proteins, such as protamine from Fluid-phase endocytosis (micropinocytosis) provides
salmon sperm (molecular weight ~4500 Da), can also transporter-independent entry to the brain for larger,
hydrophilic molecules. This process involves the uptake
88
penetrate the BBB through AMT. Cationized albumin
96
(isoelectric point = 8.5 – 9) can be conjugated to liposomes of ECF and dissolved solutes, rather than requiring
to facilitate interaction with endothelial cells. 114,115 In the molecule to interact with the endothelial plasma
addition, the lectin wheat germ agglutinin can enter the membrane. For instance, albumin can cross the BBB
95
brain through AMT. However, the cationic modification through fluid-phase endocytosis. Under homeostatic
95
also increases systemic clearance. In the B-B barrier conditions, albumin passes through the endothelial
endothelium, Non-specific transcytosis happens very layer from the luminal side to the interstitium through
seldom and would need distinct molecular signatures than an energy-dependent process mediated by vesicles.
those found in peripheral endothelial cells. In both RMT This transport can occur through vesiculo-vacuolar
88
and AMT, the payload is internalized from the plasma organelles or caveolae. 117,118 Albumin binds to the albondin
membrane of endothelial cells into endosomes, followed receptor, which facilitates its endocytosis by endothelial
by the fusion of late endosomes with lysosomes and the cells. 119,120 The binding of albumin to albondin triggers
digestion of the cargo through the endolysosomal pathway. receptor clustering and interaction with caveolin-1, a
121
This process ultimately reduces the transcytosis rate into multifunctional protein critical for caveolae formation.
the brain parenchyma. 12 It is important to note that plasma proteins, particularly
albumin, are toxic to brain cells, 122 and disruption of the
CMT is a saturable, active transport mechanism that BBB may lead to the influx of plasma into the brain.
facilitates the movement of polar molecules across the BBB.
It is involved in the transport of relatively smaller molecules 11. Extent of plasma protein binding and
such as glucose (180 Da) through GLUT1, large neutral CNS bioavailability
amino acids through LAT1, and gamma-aminobutyric
acid throu12gh GABA transporter 2. Polar drugs, such as The percentage of plasma protein binding helps assess the
levodopa (197.2 Da), gabapentin (171.24 Da), hormones, clearance and volume of distribution of a drug and predict
and fatty acids are also transported through CMT. 12,100,116 the likelihood of drug-drug interactions and the PK/PD
These transporters are highly stereoselective. While relationship. 123,124 Like other plasma proteins, albumin does
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 63 doi: 10.36922/an.5140