Page 63 - AN-4-2
P. 63
Advanced Neurology Brain bioavailability of targeted protein degraders
(BMECs) differ from other endothelial cells in that they expressed in the liver, OATP1A4 has also been detected
have a relatively higher concentration of mitochondria in both the apical and basolateral sides of the endothelial
and are virtually devoid of fenestrations. 32,33 As a result, cells of the BBB. It mediates the uptake of drugs from both
except for small lipophilic molecules, BMECs prevent the brain and the blood compartments. 41,42 Predominantly
most biological and chemical molecules from entering the expressed in the kidneys, small amounts of OAT1 are also
34
brain. Gated by tight junction proteins, the BBB prevents present in the brain cortex, hypothalamus, hippocampus,
hydrophilic molecules, charged moieties, peptides, and and cerebellum. OAT1 interacts with a broad spectrum
proteins from entering the brain, thus playing a crucial of drugs, including β-lactam antibiotics (e.g., penicillins,
role in protecting the brain parenchyma from xenobiotics benzylpenicillin, carbenicillin), immunomodulators
and other exogenous compounds. Hydrophobic, low (e.g., methotrexate), and anti-hypercholesteremic drugs
35
molecular weight compounds can diffuse across brain (fluvastatin, pravastatin, bezafibrate). 43
endothelial cells, but larger molecular weight compounds It is noteworthy that the BBB was once conceived purely
are predominantly shuttled back into circulation by efflux as a neurovascular unit. However, following the discovery
transporters, resulting in pharmacologically insignificant that the cytochrome P450 enzymes and transporters in
brain absorption. 36,37 endothelial cells regulate the rate and extent of substances
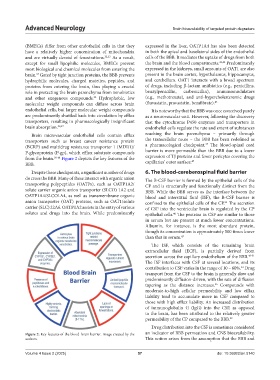
Brain microvascular endothelial cells contain efflux reaching the brain parenchyma – primarily through
transporters such as breast cancer resistance protein the transcellular route – the BBB has been redefined as
44
(BCRP) and multidrug resistance transporter 1 (MDR1)/ a pharmacological checkpoint. The blood-spinal cord
P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which efflux substrate compounds barrier is more permeable than the BBB due to a lower
from the brain. 38-40 Figure 2 depicts the key features of the expression of TJ proteins and fewer pericytes covering the
45
BBB. capillaries’ outer surface.
Despite these checkpoints, a significant number of drugs 6. The blood-cereberospinal fluid barrier
do cross the BBB. Many of these interact with organic anion The B-CSF barrier is formed by the epithelial cells of the
transporting polypeptides (OATPs), such as OATP1A2/ CP and is structurally and functionally distinct from the
solute carrier organic anion transporter (SLCO) 1A2 and BBB. While the BBB serves as the interface between the
OATP1A4/SLCO1A4, as well as transmembrane organic blood and interstitial fluid (ISF), the B-CSF barrier is
anion transporter (OAT) proteins, such as OAT1/solute confined to the epithelial cells of the CP. The secretion
36
carrier (SLC) 22A6. OATP1A2 assists in the entry of various of CSF into the ventricular brain is regulated by the CP
solutes and drugs into the brain. While predominantly epithelial cells. The proteins in CSF are similar to those
46
in serum but are present at much lower concentrations.
Albumin, for instance, is the most abundant protein,
though its concentration is approximately 500 times lower
than that in serum. 47
The ISF, which consists of the remaining brain
extracellular fluid (ECF), is partially derived from
secretion across the capillary endothelium of the BBB. 48-51
The ISF interfaces with CSF at several locations, and its
contribution to CSF varies in the range of 10 – 60%. Drug
12
transport from the CSF to the brain is generally slow and
predominantly diffusion-driven, with the rate of diffusion
tapering as the distance increases. Compounds with
36
moderate-to-high cellular permeability and low efflux
liability tend to accumulate more in CSF compared to
those with high efflux liability. An increased distribution
of immunoglobulin G (IgG) into the CSF, as opposed
to the brain, has been attributed to the relatively greater
permeability of the CP compared to the BBB. 52
Drug distribution into the CSF is sometimes considered
Figure 2. Key features of the blood–brain barrier. Image created by the an indicator of BBB permeation and CNS bioavailability.
authors. This notion arises from the assumption that the BBB and
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 57 doi: 10.36922/an.5140