Page 56 - ARNM-1-2
P. 56
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Image fusion’s significance in medicine
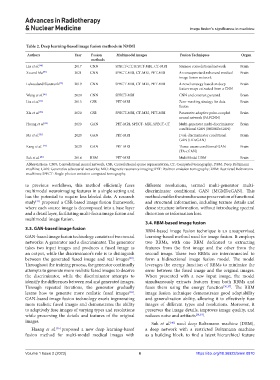
Table 2. Deep learning‑based image fusion methods in NMMI
Authors Year Fusion Multimodal images Fusion Techniques Organ
methods
Liu et al. [48] 2017 CNN SPECT-CT, SPECT-MRI, CT-MRI Siamese convolutional network Brain
Xu and Ma [49] 2021 CNN SPECT-MRI, CT-MRI, PET-MRI An unsupervised enhanced medical Brain
image fusion network
Lahoudand Süsstrunk [28] 2019 CNN SPECT-MRI, CT-MRI, PET-MRI A novel strategy based on deep Brain
feature maps extracted from a CNN
Wang et al. [30] 2020 CNN SPECT-MRI CNN and contrast pyramid Brain
Liu et al. [32] 2015 CSR PET-MRI Zero-masking strategy for data Brain
fusion
Xia et al. [50] 2020 CSR SPECT-MRI, CT-MRI, PET-MRI Parameter-adaptive pulse-coupled Brain
neural network (PAPCNN)
Huang et al. [35] 2020 GAN PET-MRI, SPECT- MRI, SPECT-CT Multi-generator multi-discriminator Brain
conditional GAN (MGMDcGAN)
Ma et al. [51] 2020 GAN PET-MRI Dual-discriminator conditional Brain
GAN (DDcGAN)
Kang et al. [52] 2020 GAN PET-MRI Tissue-aware conditional GAN Brain
(TA-cGAN)
Suk et al. [40] 2014 RBM PET-MRI MultiModal DBM Brain
Abbreviations: CNN: Convolutional neural network; CSR: Convolutional sparse representation; CT: Computed tomography; DBM: Deep Boltzmann
machine; GAN: Generative adversarial networks; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; PET: Positron emission tomography; RBM: Restricted Boltzmann
machines; SPECT: Single-photon emission computed tomography.
to previous workflows, this method efficiently fuses different resolutions, termed multi-generator multi-
multimodal neuroimaging features in a single setting and discriminator conditional GAN (MGMDcGAN). This
has the potential to require less labeled data. A research method enables the simultaneous preservation of functional
study proposed a CSR-based image fusion framework, and structural information, including texture details and
[31]
where each source image is decomposed into a base layer dense structure information, without introducing spectral
and a detail layer, facilitating multi-focus image fusion and distortion or information loss.
multimodal image fusion.
3.4. RBM-based image fusion
3.3. GAN-based image fusion RBM-based image fusion technique is an unsupervised
GAN-based image fusion technology consists of two neural learning-based method used for image fusion. It employs
networks: A generator and a discriminator. The generator two RBMs, with one RBM dedicated to extracting
takes two input images and produces a fused image as features from the first image and the other from the
an output, while the discriminator’s role is to distinguish second image. These two RBMs are interconnected to
between the generated fused image and real images . form a bidirectional image fusion model. The model
[33]
Throughout the training process, the generator continually leverages the energy function of RBMs to minimize the
attempts to generate more realistic fused images to deceive error between the fused image and the original images.
the discriminator, while the discriminator attempts to When presented with a new input image, the model
identify the differences between real and generated images. simultaneously extracts features from both RBMs and
Through repeated iterations, the generator gradually fuses them using the energy function [36,37] . The RBM
learns how to generate more realistic fused images . image fusion technique demonstrates good adaptability
[34]
GAN-based image fusion technology excels ingenerating and generalization ability, allowing it to effectively fuse
more realistic fused images and demonstrates the ability images of different types and resolutions. Moreover, it
to adaptively fuse images of varying types and resolutions preserves the image details, improves image quality, and
while preserving the details and features of the original reduces noise and artifacts [38,39] .
images. Suk et al. used deep Boltzmann machine (DBM),
[40]
Huang et al. [35] proposed a new deep learning-based a deep network with a restricted Boltzmann machine
fusion method for multi-modal medical images with as a building block, to find a latent hierarchical feature
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.0870