Page 25 - ARNM-2-1
P. 25
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Is 5-mm PTV margin 4D-CT-based radiotherapy
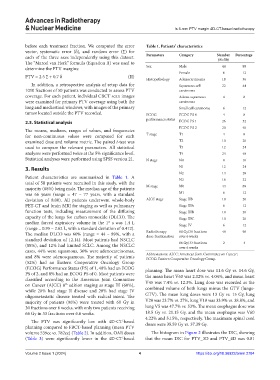
before each treatment fraction. We computed the error Table 1. Patients’ characteristics
vector, systematic error (δ), and random error (∑) for
each of the three axes independently using this dataset. Parameters Category Number Percentage
(N=50)
The “Marcel van Herk” formula (Equation II) was used to
determine the PTV margins: Sex Male 44 88
Female 6 12
PTV = 2.5 ∑ + 0.7 δ (II)
Histopathology Adenocarcinoma 18 36
In addition, a retrospective analysis of setup data for Squamous cell 22 44
1010 fractions of 50 patients was conducted to assess PTV carcinoma
coverage. For each patient, individual CBCT scan images Adeno-squamous 4 8
were examined for primary PTV coverage using both the carcinoma
lung and mediastinal windows, with images of the primary Small cell carcinoma 6 12
tumor located outside the PTV recorded. ECOG ECOG PS 0 4 8
performance status
2.3. Statistical analysis ECOG PS 1 26 52
ECOG PS 2 20 40
The means, medians, ranges of values, and frequencies
for non-continuous values were computed for each T stage T1 4 8
examined dose and volume metric. The paired t-test was T2 10 20
used to compare the relevant parameters. All statistical T3 12 24
analyses were performed twice at the 5% significance level. T4 24 48
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 21. N stage N0 8 16
3. Results N1 12 24
N2 14 28
Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1. A N3 16 32
total of 50 patients were recruited in this study, with the
majority (88%) being male. The median age of the patients M stage M0 44 88
was 66 years (range = 47 – 77 years, with a standard M1 6 12
deviation of 8.00). All patients underwent whole-body AJCC stage Stage IIB 10 20
PET-CT and brain MRI for staging as well as pulmonary Stage IIIA 6 12
function tests, including measurement of the diffusing Stage IIIB 18 36
capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO). The Stage IIIC 10 20
st
median forced expiratory volume in the 1 s was 1.4 L Stage IV 6 12
(range = 0.95 – 2.62 L, with a standard deviation of 0.412).
The median DLCO was 60% (range = 44 – 89%, with a Radiotherapy 60 Gy/30 fractions 48 96
over 6 weeks
dose-fractionation
standard deviation of 12.14). Most patients had NSCLC
(88%), and 12% had limited SCLC. Among the NSCLC 66 Gy/33 fractions 2 4
over 6 weeks
cases, 44% were squamous, 36% were adenocarcinomas,
and 8% were adenosquamous. The majority of patients Abbreviations: AJCC: American Joint Committee on Cancer;
ECOG: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group.
(52%) had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
(ECOG) Performance Status (PS) of 1, 40% had an ECOG planning. The mean heart dose was 11.6 Gy vs. 14.6 Gy,
PS of 2, and 8% had an ECOG PS of 0. Most patients were the mean heart V60 was 2.02% vs. 4.04%, and mean heart
classified according to the American Joint Committee V45 was 7.4% vs. 12.3%. Lung dose was recorded as the
on Cancer (AJCC) 8 edition staging as stage III (60%),
th
while 20% had stage II disease and 20% had stage IV combined volume of both lungs minus the GTV (lungs-
oligometastatic disease treated with radical intent. The GTV). The mean lung doses were 13 Gy vs. 15 Gy, lung
majority of patients (96%) were treated with 60 Gy in V20 was 23.7% vs. 27%, lung V10 was 33.9% vs. 38.8%, and
30 fractions over 6 weeks, with only two patients receiving lung V5 was 47.7% vs. 53%. The mean esophagus dose was
66 Gy in 33 fractions over 6.6 weeks. 18.5 Gy vs. 21.15 Gy, and the mean esophagus was V60
4.22% and 5.15%, respectively. The maximum spinal cord
The PTV was significantly low with 4D-CT-based doses were 35.59 Gy vs. 37.39 Gy.
planning compared to FBCT-based planning (mean PTV
volume 539cc vs. 782cc) (Table 2). In addition, OAR doses The histogram in Figure 2 illustrates the DIC, showing
(Table 3) were significantly lower in the 4D-CT-based that the mean DIC for PTV_3D and PTV_4D was 0.81
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/arnm.2784