Page 50 - ARNM-2-3
P. 50
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Image-guided interventional radiotherapy
and alignment of the source applicator according to 5. CT-sim guided radioactive seed
predetermined specifications. This evolution has propelled implantation
HDR-BT into a new era characterized by 3D treatment
approaches, with CT-sim scan technology playing a The CT-guided radioactive 125I seed implantation
pivotal role. Typically, HDR-BT entails 4 – 6 sessions brachytherapy utilizes imaging guidance techniques to
administered biweekly over an extended therapy duration. accurately position radioactive iodine-125 seed (with
However, the repeated insertions of the source applicator a half-life of 59.6 days, size of 0.8 × 4.5 mm, energy of
may pose a risk of cross-contamination and compromise 27 – 35 keV, and encased in a nickel-titanium alloy) within
patient tolerability. Attempts have been made to address or around tumors. The precise emission of low-energy
these challenges by converting the CT simulation room gamma rays from iodine-125 seed effectively eradicates
into an operating theater equipped with aseptic lighting tumor cells. This approach is characterized by the delivery
and imaging guidance devices, aligned with surgical of localized high doses, rapid dose decay, and minimal
standards requirements, to minimize nosocomial damage to surrounding normal tissues, establishing it as
infections. In addition, the concept of “no pain HDR-BT” an internationally recognized standard for the treatment of
was introduced, involving the utilization of an anesthesia early-stage prostate cancer. 27-32
pump to administer spinal or epidural anesthesia, ensuring In 2001, Professor Junjie Wang spearheaded the
optimal patient position comfort during treatment. implementation of this technique in China with an initial
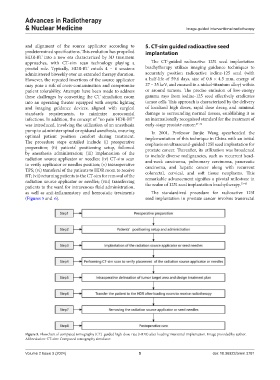
The procedure steps entailed include (i) preoperative emphasis on ultrasound-guided 125I seed implantation for
preparation; (ii) patients’ positioning setup, followed prostate cancer. Thereafter, its utilization was broadened
by anesthesia administration; (iii) implantation of the to include diverse malignancies, such as recurrent head-
radiation source applicator or needles; (iv) CT-sim scan and-neck carcinoma, pulmonary carcinoma, pancreatic
to verify applicator or needles position; (v) intraoperative carcinoma, and hepatic cancer along with recurrent
TPS; (vi) transferal of the patients to HDR room to receive colorectal, cervical, and soft tissue neoplasms. This
RT; (vii) returning patients to the CT-sim for removal of the remarkable advancement signifies a pivotal milestone in
radiation source applicator or needles; (viii) transferring the realm of 125I seed implantation brachytherapy. 33-45
patients to the ward for intravenous fluid administration,
as well as anti-inflammatory and hemostatic treatments The standardized procedure for radioactive 125I
(Figures 5 and 6). seed implantation in prostate cancer involves transrectal
Figure 5. Flowchart of computed tomography (CT)-guided high-dose-rate (HDR) after-loading interstitial implantation. Image provided by author.
Abbreviation: CT-sim: Computed tomography simulator.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3781