Page 51 - ARNM-2-3
P. 51
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Image-guided interventional radiotherapy
ultrasound guidance, real-time intraoperative planning, planning poses challenges due to the presence of organ at
and high-precision single-session completion. 46,47 risk (OAR), including bones, blood vessels, trachea, and
CT-guided techniques were applied in the field of 125I intestines; (ii) Ultrasound-guided 125I seed implantation
seed implantation in 2002. 44,46-52 The advantages of CT for prostate cancer mainly relies on two-dimensional plans
guidance are as follows: (i) high-resolution CT scans; with needles inserted parallelly, which could not apply to
and (ii) unaffected by bone or gas interference, allowing the other part of the body; (iii) The absence of a 3D planning
treatment of lung cancer, head-and-neck, pelvis, and system limits the ability to achieve 125I seed distribution
spinal cord with 125I seed implantation. Nonetheless, in 3D space across different locations of the carcinoma.
certain drawbacks must be acknowledged: (i) Preoperative In 2015, Chinese physicians independently spearheaded
the development of radioactive seed implant fixation and
A B navigation brackets, in conjunction with 3D-printing non-
coplanar template (3D-PNCT) or 3D-PCT, which features
individual design and precise 125I seed implantation across
diverse tumor location. In addition, brachytherapy-TPS
(B-TPS) software compatible with 3D-PNCT or 3D-PCT
and computer planning algorithms have been developed
to ensure optimal 3D spatial distribution of radioactive
C D 125I seeds in the tumor targets. This approach enables
the fulfillment of preoperative target volume prescription
dose, while minimizing radiation exposure to OAR. As a
result of these advancements, 125I seed implantation has
achieved standardization and uniformity in the treatment
of solid tumors throughout the body, emerging as a widely
applicable standardized protocol and possessing significant
Figure 6. CT-sim guided HDR high-dose-rate after-loading
brachytherapy. (A) Preoperative preparation; (B) Implantation applicator; advantages in the management of recurrent head-and-neck
(C) Target delineation and pre-planning; (D) Radiotherapy in high-dose- cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, recurrent pelvic
rate (HDR) after-loading room. Image provided by author. carcinoma, soft tissue tumors, and other conditions. 53-60
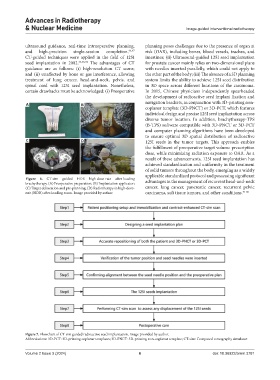
Figure 7. Flowchart of CT-sim guided radioactive seed implantation. Image provided by author.
Abbreviations: 3D-PCT: 3D-printing coplanar templates; 3D-PNCT: 3D-printing non-coplanar template; CT-sim: Computed tomography simulator.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3781