Page 58 - ARNM-2-4
P. 58
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Efficacy of stereotactic radiotherapy
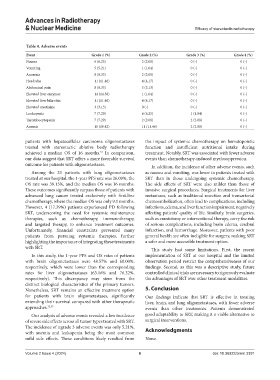
Table 4. Adverse events
Event Grade 1 (%) Grade 2 (%) Grade 3 (%) Grade 4 (%)
Nausea 6 (6.25) 2 (2.08) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Vomiting 5 (5.21) 1 (1.04) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Anorexia 8 (8.33) 2 (2.08) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Headache 11 (11.46) 4 (4.17) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Abdominal pain 8 (8.33) 3 (3.13) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Elevated liver enzymes 14 (14.58) 1 (1.04) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Elevated liver bilirubin 11 (11.46) 4 (4.17) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Elevated creatinine 3 (3.13) 0 (-) 0 (-) 0 (-)
Leukopenia 7 (7.29) 6 (6.25) 1 (1.04) 0 (-)
Thrombocytopenia 7 (7.29) 2 (2.08) 2 (2.08) 0 (-)
Anemia 10 (10.42) 11 (11.46) 2 (2.08) 0 (-)
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma oligometastases the impact of systemic chemotherapy on hematopoietic
treated with stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy function and insufficient nutritional intake during
achieved a median OS of 16 months. In comparison, treatment. Notably, SRT was associated with fewer adverse
31
our data suggest that SRT offers a more favorable survival events than chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression.
outcome for patients with oligometastases. In addition, the incidence of other adverse events, such
Among the 23 patients with lung oligometastases as nausea and vomiting, was lower in patients treated with
treated at our hospital, the 1-year PFS rate was 26.09%, the SRT than in those undergoing systemic chemotherapy.
OS rate was 39.13%, and the median OS was 16 months. The side effects of SRT were also milder than those of
These outcomes significantly surpass those of patients with invasive surgical procedures. Surgical treatments for liver
advanced lung cancer treated exclusively with first-line metastases, such as traditional resection and transarterial
chemotherapy, where the median OS was only 9.1 months. chemoembolization, often lead to complications, including
However, 4 (17.39%) patients experienced PD following infections, edema, and liver function impairment, negatively
SRT, underscoring the need for systemic maintenance affecting patients’ quality of life. Similarly, brain surgeries,
therapies, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, such as craniotomy or interventional therapy, carry the risk
and targeted therapy, to enhance treatment outcomes. of serious complications, including brain edema, cerebral
Unfortunately, financial constraints prevented many infarction, and hemorrhage. Moreover, patients with poor
patients from pursuing systemic therapies, further general health are often ineligible for surgery, making SRT
highlighting the importance of integrating these treatments a safer and more accessible treatment option.
with SRT. This study had some limitations. First, the recent
In this study, the 1-year PFS and OS rates of patients implementation of SRT at our hospital and the limited
with brain oligometastases were 48.57% and 60.00%, observation period restrict the comprehensiveness of our
respectively, which were lower than the corresponding findings. Second, as this was a descriptive study, future
rates for liver oligometastases (63.16% and 76.32%, controlled clinical trials are necessary to rigorously evaluate
respectively). This discrepancy may stem from the the advantages of SRT over other treatment modalities.
distinct biological characteristics of the primary tumors.
Nonetheless, SRT remains an effective treatment option 5. Conclusion
for patients with brain oligometastases, significantly Our findings indicate that SRT is effective in treating
extending their survival compared with other therapeutic liver, brain, and lung oligometastases, with fewer adverse
approaches. 32,33 events than other treatments. Patients demonstrated
Our analysis of adverse events revealed a low incidence good adaptability to SRT, making it a viable alternative to
of severe side effects across all tumor types treated with SRT. surgical interventions.
The incidence of ≥grade 3 adverse events was only 5.21%,
with anemia and leukopenia being the most common Acknowledgments
mild side effects. These conditions likely resulted from None.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3391