Page 67 - ARNM-2-4
P. 67
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Different approaches for the computation of BED
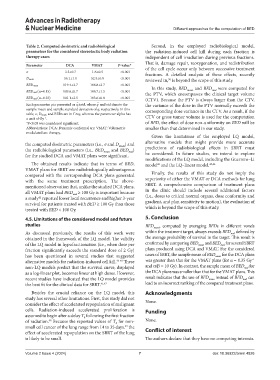
Table 2. Computed dosimetric and radiobiological Second, in the employed radiobiological model,
parameters for the considered stereotactic body radiation the radiation-induced cell kill during each fraction is
therapy cases independent of cell irradiation during previous fractions.
That is, damage repair, reoxygenation, and redistribution
Parameter DCA VMAT P-value*
of the cell cycle occur only between successive treatment
σ 3.5±0.7 1.6±0.5 <0.001 fractions. A detailed analysis of these effects, recently
50
Dmean 56.1±1.1 52.9±0.9 <0.001 reviewed in, is beyond the scope of this study.
BEDmean 119.4±3.7 108.8±2.7 <0.001 In this study, BED and BED were computed for
mean
nud
BEDnud (α=0.15) 109.6±0.7 106.7±1.5 <0.001 the PTV, which encompasses the clinical target volume
BEDnud (α=0.35) 101.1±2.5 103.6±0.8 <0.001 (CTV). Because the PTV is always larger than the CTV,
–
–
Each parameter q is presented as q±std, where q and std denote the the variance of the dose in the PTV normally exceeds the
sample mean and sample standard deviation of q, respectively. In this corresponding dose variance in the CTV. As a result, if the
table, σ, Dmean, and BEDs are in Gray, whereas the parameter alpha has
a unit of Gy . CTV or gross tumor volume is used for the computation
−1
*P<0.05 was considered significant. of BED, the effect of dose non-uniformity on BED will be
Abbreviations: DCA: Dynamic conformal arc; VMAT: Volumetric smaller than that determined in our study.
modulated arc therapy.
Given the limitations of the employed LQ model,
the computed dosimetric parameters (i.e., σ and D mean ) and alternative models that might provide more accurate
the radiobiological parameters (i.e., BED mean and BED ) predictions of radiobiological effects in SBRT must
nud
for the studied DCA and VMAT plans were significant. be considered. In future studies, we intend to explore
modifications of the LQ model, including the Guerrero–Li
The obtained results indicate that in terms of BED, model and the LQ–linear model. 45,46
43
VMAT plans for SBRT are radiobiologically advantageous
compared with the corresponding DCA plans generated Finally, the results of this study do not imply the
with the same treatment prescription. The above- superiority of either the VMAT or DCA methods for lung
mentioned observation that, unlike the studied DCA plans, SBRT. A comprehensive comparison of treatment plans
all VMAT plans had BED nud ≥ 100 Gy is important because in the clinic should include several additional factors
42
a study reported lower local recurrence and higher 3-year (i.e., doses to critical normal organs, dose conformity and
survival for patients treated with BED ≥ 100 Gy than those gradient, and plan sensitivity to motion), the evaluation of
treated with BED < 100 Gy. which is beyond the scope of this study.
4.5. Limitations of the considered model and future 5. Conclusion
studies BED mean , computed by averaging BEDs in different voxels
As discussed previously, the results of this work were within the treatment target, always exceeds BED defined by
nud
obtained in the framework of the LQ model. The validity the average probability of survival in the target. This result is
of the LQ model in hypofractionation (i.e., when dose per confirmed by comparing BED mean and BED for several SBRT
nud
fraction significantly exceeds the standard dose of 2 Gy) plans produced using DCA and VMAT. For the considered
has been questioned in several studies that suggested cases of SBRT, the sample mean of BED mean for the DCA plans
−1
alternative models for radiation-induced cell kill. 43-46 These was greater than that for the VMAT plans (for α = 0.35 Gy
non-LQ models predict that the survival curve, displayed and α/b = 10 Gy). In contrast, the sample mean of BED for
nud
as a log-linear plot, becomes linear at high doses. However, the DCA plans was smaller than that for the VMAT plans. This
recent studies have indicated that the LQ model provides result indicates that the use of BED mean instead of BED can
nud
the best fit for the clinical data for SBRT. 41,47 lead to an incorrect ranking of the compared treatment plans.
Besides the crucial reliance on the LQ model, this Acknowledgments
study has several other limitations. First, this study did not
consider the effect of accelerated repopulation of malignant None.
cells. Radiation-induced accelerated proliferation is Funding
assumed to begin after a delay T following the first fraction
k
of radiation. Because the reported values of T for non- None.
48
k
49
small cell cancer of the lung range from 14 to 35 days. the
effect of accelerated repopulation on the SBRT of the lung Conflict of interest
is likely to be small. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/arnm.4826