Page 114 - ARNM-3-1
P. 114
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine 18 F-FDG PET & unexplained inflammatory syndromes
persist for several weeks or even months, evolving into empirical corticosteroid or antibiotic therapy, leading
chronic inflammation, where vascular congestion is less to false-negative results. An example from our study
pronounced. During this phase, neutrophils in the exudate is a patient with Horton’s disease under corticosteroid
either undergo apoptosis or migrate back into the vascular treatment, who exhibited a negative F-FDG PET scan.
18
environment. They are gradually replaced by macrophages 18 FDG PET/CT is a valuable tool for identifying the
and lymphocytes, leading to fibrotic changes in the affected etiology of inflammatory syndromes, with a wide range of
tissues. When phagocytic cells (primarily neutrophils, indications. This includes gastrointestinal infections, such
1
eosinophils, and monocytes) are exposed to certain as inflammatory colitis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative
stimuli, they metabolize large amounts of glucose through colitis (Figure 2), as well as granulomatous diseases such as
aerobic or anaerobic glycolysis, a phenomenon known as sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. In this context, F-FDG PET/CT
18
the “respiratory explosion.” This process triggers cellular demonstrates high sensitivity but relatively lower specificity. 3,4
defense mechanisms, including migration, microbicide
2
production, and phagocytosis. Consequently, cellular In infectious diseases, 18 F-FDG PET/CT is
18
uptake of F-FDG increases, a process further enhanced particularly effective in diagnosing diabetic foot infections,
by cytokine- and growth factor-induced upregulation of osteomyelitis, and prosthetic joint infections, with high
glucose transporters. There is no fundamental difference specificity. Beyond enabling etiological diagnosis, it also
1,2
between the mechanisms of F-FDG uptake and metabolic facilitates assessments of infection extent and therapeutic
18
trapping in inflammatory and neoplastic cells (Figure 1). monitoring, underscoring its significant medico-economic
5-10
In both cases, radiotracer accumulation occurs due to value.
increased expression of membrane transporters, elevated
cellular energy consumption, and inability to metabolize A B
fluorinated glucose.
Furthermore, there is no inherent limitation to the use of
SUVmax as a semi-quantitative index in F-FDG PET/CT.
18
This is due to the potential for intense F-FDG uptake
18
in highly active inflammatory or infectious pathologies,
such as sarcoidosis or tuberculosis. Conversely, low or
18
absent F-FDG uptake may occur in patients undergoing
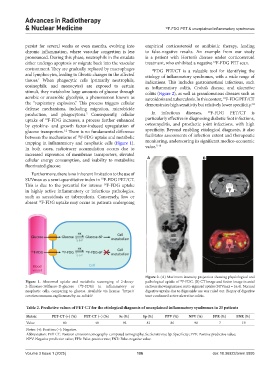
Figure 2. (A) Maximum intensity projection showing physiological and
Figure 1. Abnormal uptake and metabolic scavenging of 2-deoxy- pathological uptake of F-FDG. (B) CT image and fusion image in axial
18
2-[fluorine-18]fluoro-D-glucose ( F-FDG) in inflammatory or sections showing intense recto-sigmoid uptake (SUVmax = 16.4). Normal
18
neoplastic cells, comparing to glucose. Available via license: “https:// digestive uptake due to Biguanide use was ruled out. Biopsy of digestive
creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ tract confirmed active ulcerative colitis.
Table 2. Predictive values of PET-CT for the etiological diagnosis of unexplained inflammatory syndromes in 25 patients
Metric PET-CT (+) (%) PET-CT (−) (%) Se (%) Sp (%) PPV (%) NPV (%) FPR (%) FNR (%)
Value 60 40 93 81 86 90 7 19
Notes: (+): Positive; (−): Negative.
Abbreviation: PET-CT: Positron emission tomography-computed tomography; Se: Sensitivity; Sp: Specificity; PPV: Positive predictive value;
NPV: Negative predictive value; FPR: False-positive rate; FNR: False-negative value.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 106 doi: 10.36922/arnm.5895