Page 115 - ARNM-3-1
P. 115
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine 18 F-FDG PET & unexplained inflammatory syndromes
A B C
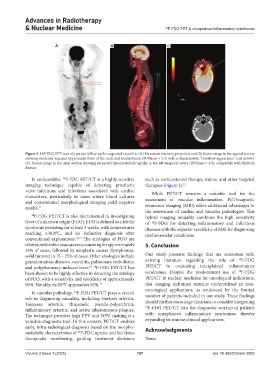
Figure 3. 18F-FDG PET scan of a patient follow-up for suspected vasculitis. (A) Maximum intensity projection and (B) fusion image in the sagittal section
showing moderate vascular hypermetabolism of the neck and mediastinum (SUVmax = 5.3) with a characteristic “crossbow appearance” (red arrow).
(C) Fusion image in the axial section showing suspected hypermetabolic uptake in the left temporal artery (SUVmax = 4.5), compatible with Horton’s
disease.
In endocarditis, F-FDG PET/CT is a highly sensitive such as corticosteroid therapy, statins, and other targeted
18
imaging technique capable of detecting prosthetic therapies (Figure 3). 15
valve infections and infections associated with cardiac While PET/CT remains a valuable tool for the
stimulators, particularly in cases where blood cultures assessment of vascular inflammation, PET/magnetic
and conventional morphological imaging yield negative
results. 11 resonance imaging (MRI) offers additional advantages in
the assessment of cardiac and vascular pathologies. This
18 F-FDG PET/CT is also instrumental in investigating hybrid imaging modality combines the high sensitivity
fever of unknown origin (FUO). FUO is defined as a febrile of F-FDG for detecting inflammatory and infectious
18
syndrome persisting for at least 3 weeks, with temperatures diseases with the superior specificity of MRI for diagnosing
reaching ≥38.8°C, and no definitive diagnosis after cardiovascular conditions.
conventional explorations. 12,13 The etiologies of FUO are
diverse, with infectious causes accounting for approximately 5. Conclusion
25% of cases, followed by neoplastic causes (lymphomas,
solid tumors) in 15 – 25% of cases. Other etiologies include Our study presents findings that are consistent with
granulomatous diseases, vasculitis, pulmonary embolisms, existing literature regarding the role of 18 F-FDG
and polypharmacy-induced fever. F-FDG PET/CT has PET/CT in evaluating unexplained inflammatory
14 18
18
been shown to be highly effective in detecting the etiology syndromes. Despite the predominant use of F-FDG
of FUO, with a sensitivity and specificity of approximately PET/CT in nuclear medicine for oncological indications,
90%. Notably, its NPV approaches 95%. 14 this imaging technique remains underutilized in non-
oncological applications, as evidenced by the limited
In vascular pathology, F-FDG PET/CT plays a crucial
18
role in diagnosing vasculitis, including Horton’s arteritis, number of patients included in our study. These findings
Takayasu arteritis, rhizomelic pseudo-polyarthritis, should further encourage clinicians to consider integrating
18
inflammatory arteritis, and active atheromatous plaques. F-FDG PET/CT into the diagnostic workup of patients
The technique provides high PPV and NPV, making it a with unexplained inflammatory syndromes, thereby
valuable diagnostic tool. In this context, PET/CT enables expanding its routine clinical applications.
early, infra-radiological diagnosis based on the morpho- Acknowledgments
metabolic characteristics of F-FDG uptake and facilitates
18
therapeutic monitoring, guiding treatment decisions None.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 107 doi: 10.36922/arnm.5895