Page 113 - ARNM-3-1
P. 113
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine 18 F-FDG PET & unexplained inflammatory syndromes
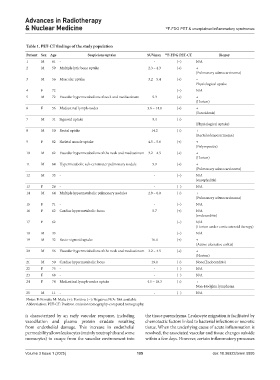
Table 1. PET-CT findings of the study population
Patient Sex Age Suspicions uptake SUVmax 18 F-FDG PET-CT Biopsy
1 M 61 - - (−) N/A
2 M 59 Multiple lytic bone uptake 2.3 – 4.3 (+) +
(Pulmonary adenocarcinoma)
3 M 56 Muscular uptake 3.2 – 5.4 (+) −
Physiological uptake
4 F 72 - - (−) N/A
5 M 72 Vascular hypermetabolism of neck and mediastinum 5.3 (+) +
(Horton)
6 F 56 Mediastinal lymph-nodes 3.6 – 14.8 (+) +
(Sarcoidosis)
7 M 31 Sigmoid uptake 9.4 (+) −
(Physiological uptake)
8 M 50 Rectal uptake 14.2 (+) +
(Rectal adenocarcinoma)
9 F 82 Skeletal muscle uptake 4.5 – 5.6 (+) +
(Polymyositis)
10 M 62 Vascular hypermetabolism of the neck and mediastinum 3.2 – 4.5 (+) +
(Horton)
11 M 64 Hypermetabolic sub-centimeter pulmonary nodule 5.9 (+) +
(Pulmonary adenocarcinoma)
12 M 33 - - (−) N/A
(encephalitis)
13 F 26 - - (−) N/A
14 M 64 Multiple hypermetabolic pulmonary nodules 2.9 – 6.0 (+) +
(Pulmonary adenocarcinoma)
15 F 71 - - (−) N/A
16 F 62 Cardiac hypermetabolic focus 5.7 (+) N/A
(endocarditis)
17 F 62 - - (−) N/A
(Horton under corticosteroid therapy)
18 M 33 - - (−) N/A
19 M 32 Recto-sigmoid uptake 16.4 (+) +
(Active ulcerative colitis)
20 M 56 Vascular hypermetabolism of the neck and mediastinum 3.2 – 4.5 (+) +
(Horton)
21 M 50 Cardiac hypermetabolic focus 19.0 (+) None(Endocarditis)
22 F 75 - - (−) N/A
23 F 68 - - (−) N/A
24 F 74 Mediastinal lymph-nodes uptake 4.5 – 10.3 (+) +
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
25 M 11 - - (−) N/A
Notes: F: Female; M: Male; (+): Positive; (−): Negative; N/A: Not available.
Abbreviation: PET-CT: Positron emission tomography-computed tomography.
is characterized by an early vascular response, including the tissue parenchyma. Leukocyte migration is facilitated by
vasodilation and plasma protein exudate resulting chemotactic factors linked to bacterial infections or necrotic
from endothelial damage. This increase in endothelial tissue. When the underlying cause of acute inflammation is
permeability allows leukocytes (mainly neutrophils and some resolved, the associated vascular and tissue changes subside
monocytes) to escape from the vascular environment into within a few days. However, certain inflammatory processes
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 105 doi: 10.36922/arnm.5895