Page 108 - ARNM-3-1
P. 108
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Role of 18F-FDG in brown tumor detection
A B in their description. Additional imaging modalities, such
as CT, MRI, and/or PET/CT become necessary in cases
of diagnostic uncertainty, multifocality, or involvement of
adjacent soft tissues.
In general, 99m Tc-MIBI scintigraphy remains the gold
standard for pre-operative localization of hyperfunctional
parathyroid lesions in primary, secondary, or tertiary HPT.
4
In cases of known bone lesions, it is feasible to combine
cervical and mediastinal exploration with a whole-body
C
analysis, which allows mapping of the lesions throughout
the skeleton in a single examination. In a study by
5
Zhao and Wang, whole-body 99m Tc-MIBI scintigraphy
performed in the context of primary (63 patients) and
secondary (16 patients) HPT showed bone hyperfixations
corresponding to brown tumors in 4% of cases (3/79). These
hyperfixations are not constant, differ from one patient to
another, and are not specific to brown tumors but reflect bone
hypermetabolism related to osteoclastic cell proliferation.
6
The radiopharmaceutical accumulates in mitochondrial
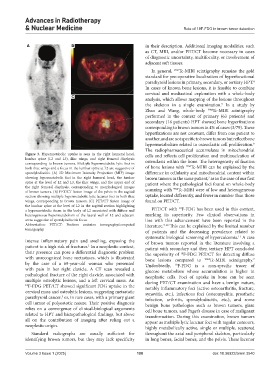
Figure 3. Hypermetabolic uptake is seen in the right humeral head, cells and reflects cell proliferation and multinucleation of
lumbar spine (L2 and L3), iliac wings, and right femoral diaphysis osteoclasts within the bone. The heterogeneity of fixation
corresponding to brown tumors. Multiple hypermetabolic lytic foci in
both iliac wings and a focus in the lumbar spine at L2 are suggestive of of bone lesions with 99m Tc-MIBI can be explained by the
spondylodiscitis. (A) 3D Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP) image difference in cellularity and mitochondrial content within
showing hypermetabolic foci in the right humeral head, the lumbar brown tumors in the same patient, as in the case of our first
7
spine at the level of L2 and L3, the iliac wings, and the upper end of patient where the pathological foci found on whole-body
the right femoral diaphysis, corresponding to morphological images scanning with 99m Tc-MIBI were of low and heterogeneous
of brown tumors. (B) PET/CT fusion image of the pelvis in the sagittal
section showing multiple hypermetabolic lytic lacunar foci in both iliac uptake, located differently, and fewer in number than those
wings, corresponding to brown tumors. (C) PET/CT fusion image of found on PET/CT.
the lumbar spine at the level of L2 in the sagittal section highlighting 18
a hypermetabolic focus in the body of L2 associated with diffuse and PET/CT with F-FDG has been used in this context,
heterogeneous hypermetabolism of the lateral wall of L2 and adjacent marking its superiority. Few clinical observations in
areas suggestive of spondylodiscitis focus. line with this advancement have been reported in the
Abbreviation: PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed literature. 7-10 This can be explained by the limited number
tomography.
of patients and the decreasing prevalence related to
systematic biological screening of hypercalcemia. A case
11
intense inflammatory pain and swelling, exposing the of brown tumors reported in the literature involving a
patient to a high risk of fractures. In a neoplastic context, patient with secondary and then tertiary HPT concluded
1
their presence can pose a differential diagnostic problem the superiority of F-FDG PET/CT for detecting diffuse
18
with unrecognized bone metastases, which is illustrated bone lesions compared to 99m Tc-MIBI scintigraphy.
7
by the case of a 69-year-old woman who presented Undoubtedly, 18 F-FDG is a non-specific tracer of
with pain in her right clavicle. A CT scan revealed a glucose metabolism whose accumulation is higher in
pathological fracture of the right clavicle, associated with neoplastic cells. Foci of uptake in bone can be seen
multiple osteolytic lesions, and a left cervical mass. An during PET/CT examination and have a benign nature,
18 F-FDG PET/CT showed significant FDG uptake in the notably inflammatory foci (active osteoarthritis, fracture,
cervical mass and osteolytic lesions, suggesting metastatic synovitis, etc.), infectious foci (osteomyelitis, prosthetic
parathyroid cancer, or, in rare cases, with a primary giant infection, arthritis, spondylodiscitis, etc.), and some
3
cell tumor of polyostotic nature. Their positive diagnosis benign bone pathologies such as brown tumors, giant
relies on a convergence of clinical-biological arguments cell bone tumors, and Paget’s disease in case of malignant
related to HPT and histopathological findings, but above transformation. During this examination, brown tumors
all on the contribution of imaging after ruling out a appear as multiple lytic lacunar foci with regular contours,
neoplastic origin. highly metabolically active, single or multiple, scattered
Standard radiographs are usually sufficient for throughout the axial and peripheral skeleton, particularly
identifying brown tumors, but they may lack specificity in long bones, facial bones, and the pelvis. These lacunar
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 100 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3540