Page 58 - ARNM-3-1
P. 58
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine The novel index and osteoradionecrosis
Table 2. Definition of the combined PIV and TE groups and
PIV‑TE‑ORNJ index groups
Characteristics Definition
Combined PIV and TE groups
Group 1 PIV<833 and Pre-C-CRT TE˂4
Group 2 PIV<833 and Pre-C-CRT TE≥4
Group 3 PIV≥833 and Pre-C-CRT TE˂4
Group 4 PIV≥833 and Pre-C-CRT TE≥4
PIV-TE-ORNJ index groups
Low risk PIV<833 and Pre-C-CRT TE˂4
Intermediate risk PIV<833 and Pre-C-CRT TE≥4
High risk or PIV≥833 and Pre-C-CRT TE˂4
PIV≥833 and Pre-C-CRT TE≥4
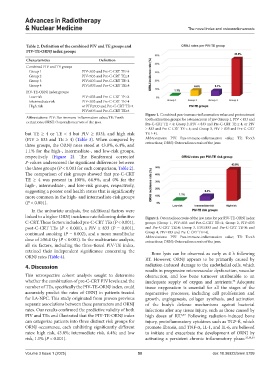
Figure 1. Combined pan-immune-inflammation value and pretreatment
Abbreviations: PIV: Pan-immune-inflammation value; TE: Tooth tooth extraction groups for osteonecrosis of jaw (Group 1, PIV < 833 and
extractions; ORNJ: Osteoradionecrosis of the jaws. Pre-C-CRT TE < 4; Group 2, PIV < 833 and Pre-C-CRT TE ≥ 4, or PIV
≥ 833 and Pre-C-CRT TE < 4; and Group 3, PIV ≥ 833 and Pre-C-CRT
but TE ≥ 4 or TE < 4 but PIV ≥ 833); and high risk TE ≥ 4).
(PIV ≥ 833 and TE ≥ 4) (Table 3). When compared by Abbreviations: PIV: Pan-immune-inflammation value; TE: Tooth
three groups, the ORNJ rates stood at 43.8%, 6.4%, and extractions; ORNJ: Osteoradionecrosis of the jaws.
1.1% for the high-, intermediate-, and low-risk groups,
respectively (Figure 2). The Bonferroni corrected
P-values underscored the significant differences between
the three groups (P < 0.001 for each comparison, Table 2).
The comparison of risk groups showed that pre-C-CRT
TE ≥ 4 was present in 100%, 64.9%, and 0% for the
high-, intermediate-, and low-risk groups, respectively,
suggesting a poorer oral health status that is significantly
more common in the high- and intermediate-risk groups
(P < 0.001).
In the univariate analysis, five additional factors were
linked to a higher ORNJ incidence rate following definitive Figure 2. Osteoradionecrosis of the jaw rates for per PIV-TE-ORNJ index
C-CRT. These factors included pre-C-CRT TEs (P < 0.001), groups (Group 1, PIV<833 and Pre-C-CRT TE˂4; Group 2, PIV<833
post-C-CRT TEs (P < 0.001), a PIV ≥ 833 (P = 0.001), and Pre-C-CRT TE≥4; Group 3, PIV≥833 and Pre-C-CRT TE˂4; and
continued smoking (P = 0.002), and a mean mandibular Group 4, PIV≥833 and Pre-C-CRT TE≥4).
dose of ≥56.4 Gy (P < 0.001). In the multivariate analysis, Abbreviations: PIV: Pan-immune-inflammation value; TE: Tooth
extractions; ORNJ: Osteoradionecrosis of the jaws.
all six factors, including the three-tiered PIV-TE index,
retained their independent significance concerning the Bone lysis can be observed as early as 4 h following
ORNJ rates (Table 4). RT. However, ORNJ appears to be primarily caused by
4. Discussion radiation-induced damage to the endothelial cells, which
results in progressive microvascular dysfunction, vascular
This retrospective cohort analysis sought to determine obstruction, and low bone turnover attributable to an
whether the combination of pre-C-CRT PIV levels and the inadequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. Adequate
36
number of TEs, specifically the PIV-TE-ORNJ index, could tissue oxygenation is essential for all the stages of the
accurately predict the rates of ORNJ in patients treated regenerative processes, including cell proliferation and
for LA-NPC. This study originated from proven previous growth, angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, and activation
separate associations between these parameters and ORNJ of the body’s defense mechanisms against bacterial
rates. Our results confirmed the predictive validity of both infections after any tissue injury, such as those caused by
PIV and TEs and illustrated that the PIV-TE-ORNJ index high doses of RT. Following radiation-induced bone
6,37
can categorize patients into three distinct risk groups for injury, proinflammatory cytokines such as TGF-ß, which
ORNJ occurrence, each exhibiting significantly different promote fibrosis, and TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, are believed
rates: high risk, 43.8%; intermediate risk, 6.4%; and low to initiate and exacerbate the development of ORNJ by
risk, 1.1% (P < 0.001). activating a persistent chronic inflammatory phase. 35,38,39
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 50 doi: 10.36922/arnm.5799