Page 53 - BH-2-3
P. 53
Brain & Heart Balloon valvuloplasty for aortic stenosis
Figure 19. Graph depicting event-free rates following balloon aortic
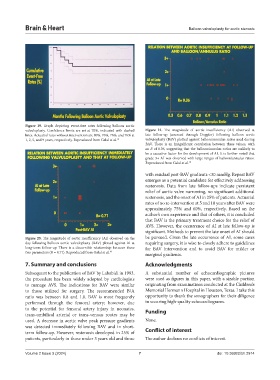
valvuloplasty. Confidence limits are set at 70%, indicated with dashed Figure 21. The magnitude of aortic insufficiency (AI) observed at
lines. Actuarial rates without intervention are 80%, 76%, 76%, and 76% at late follow-up (assessed through Doppler) following balloon aortic
1, 2, 5, and 9 years, respectively. Reproduced from Galal et al. 19 valvuloplasty (BAV) plotted against balloon/annulus ratios used during
BAV. There is an insignificant correlation between these values, with
an R of 0.36, suggesting that the balloon/annulus ratios are unlikely to
be a causative factor for the development of AI. It is further noted that
grade 3+ AI was observed with large ranges of balloon/annulus ratios.
Reproduced from Galal et al. 19
with residual post-BAV gradients <30 mmHg. Repeat BAV
emerges as a potential candidate for effectively addressing
restenosis. Data from late follow-ups indicate persistent
relief of aortic valve narrowing, no significant additional
restenosis, and the onset of AI in 25% of patients. Actuarial
rates of no re-intervention at 5 and 10 years after BAV were
approximately 75% and 60%, respectively. Based on the
author’s own experience and that of others, it is concluded
that BAV is the primary treatment choice for the relief of
AVS. However, the occurrence of AI at late follow-up is
significant. Methods to prevent the late onset of AI should
Figure 20. The magnitude of aortic insufficiency (AI) observed on the be pursued. Given the late occurrence of AI, some cases
day following balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) plotted against AI at requiring surgery, it is wise to closely adhere to guidelines
long-term follow-up. There is a discernible relationship between these for BAV intervention and to avoid BAV for milder or
two parameters (R = 0.71). Reproduced from Galal et al. 19 marginal gradients.
7. Summary and conclusions Acknowledgments
Subsequent to the publication of BAV by Lababidi in 1983, A substantial number of echocardiographic pictures
the procedure has been widely adopted by cardiologists were used as figures in this paper, with a sizable portion
to manage AVS. The indications for BAV were similar originating from examinations conducted at the Children’s
to those utilized for surgery. The recommended B/A Memorial Hermann Hospital in Houston, Texas. I take this
ratio was between 0.8 and 1.0. BAV is most frequently opportunity to thank the sonographers for their diligence
performed through the femoral artery; however, due in securing high-quality echocardiograms.
to the potential for femoral artery injury in neonates, Funding
trans-umbilical arterial or trans-venous routes may be
used. A decrease in aortic valve peak pressure gradients None.
was detected immediately following BAV and in short-
term follow-up. However, restenosis developed in 25% of Conflict of interest
patients, particularly in those under 3 years old and those The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/bh.2914