Page 52 - BH-2-4
P. 52
Brain & Heart Stem cells in cardiovascular disease
are still under development. Among the 157 recipients hold promise for improving self-healing and angiogenesis
2
of ventricular assist devices in the UK, 50% achieved a as well as for disease modeling and drug testing in HCM. 7
5-year survival rate. Stem cell therapy, with its potential Another cell type demonstrating significant potential
3
to regenerate heart tissue, provides a promising solution, in improving cardiac function is mesenchymal stem cells
opening new avenues in cardiac care. This article explores (MSCs), which improve heart tissue regeneration after
recent advancements in stem call applications for treating myocardial infarction through paracrine signaling. MSCs
CVDs, underscoring their potential to repair the damaged are adult stem cells derived from the bone marrow (BM),
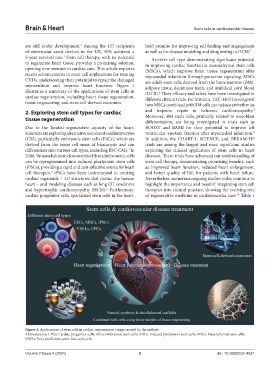
myocardium and improve heart function. Figure 1 adipose tissue, deciduous teeth, and umbilical cord blood
illustrates a summary of the applications of stem cells in (UCB). Their efficacy and safety have been investigated in
2
cardiac regeneration, including heart tissue regeneration, different clinical trials. For instance, TAC-HFT investigated
tissue engineering, and stem cell-derived exosomes. how MSCs combined with BM cells can reduce arrhythmias
8
2. Exploring stem cell types for cardiac and improve repair in ischemic cardiomyopathy.
tissue regeneration Moreover, BM stem cells, primarily related to osteoblast
differentiation, are being investigated in trials such as
Due to the limited regenerative capacity of the heart, BOOST and BAMI for their potential to improve left
scientists are exploring alternative sources of cardiomyocytes ventricular ejection fraction after myocardial infarction.
9
(CM), particularly embryonic stem cells (ESCs), which are In addition, the CHART-1, SCIENCE, and DREAM-HF
derived from the inner cell mass of blastocysts and can trials are among the largest and most significant studies
differentiate into various cell types, including ESC-CMs. In exploring the clinical application of stem cells in heart
4
2006, Yamanaka’s team demonstrated that adult somatic cells diseases. These trials have advanced our understanding of
can be reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells stem cell therapy, demonstrating promising benefits, such
(iPSCs), providing a rapid and cost-effective source for heart as improved heart function, reduced heart enlargement,
5
cell therapies. iPSCs have been instrumental in creating and better quality of life, for patients with heart failure.
cardiac organoids – 3D structures that mimic the human Nevertheless, numerous ongoing studies today continue to
heart – and modeling diseases such as long QT syndrome highlight the importance and need of integrating stem cell
6
and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Furthermore, therapies into clinical practice, showing the evolving role
10
cardiac progenitor cells, specialized stem cells in the heart, of regenerative medicine in cardiovascular care. Table 1
Figure 1. Applications of stem cells in cardiac regeneration. Image created by the authors.
Abbreviations: CPCs: Cardiac progenitor cells; ESCs: Embryonic stem cells; iPSCs: Induced pluripotent stem cells; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells;
VSELs: Very small embryonic-like stem cells.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/bh.4521