Page 12 - BH-3-1
P. 12
Brain & Heart TAVR in low gradient aortic stenosis
A
B
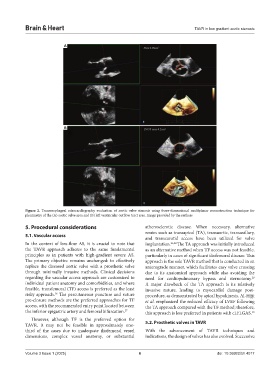
Figure 2. Transesophageal echocardiography evaluation of aortic valve stenosis using three-dimensional multiplanar reconstruction technique for
planimetry of the (A) aortic valve area and (B) left ventricular outflow tract area. Image provided by the authors
5. Procedural considerations atherosclerotic disease. When necessary, alternative
routes such as transapical (TA), transaortic, transaxillary,
5.1. Vascular access
and transcarotid access have been utilized for valve
In the context of low-flow AS, it is crucial to note that implantation. 26,28 The TA approach was initially introduced
the TAVR approach adheres to the same fundamental as an alternative method when TF access was not feasible,
principles as in patients with high-gradient severe AS. particularly in cases of significant iliofemoral disease. This
The primary objective remains unchanged: to effectively approach is the sole TAVR method that is conducted in an
replace the diseased aortic valve with a prosthetic valve anterograde manner, which facilitates easy valve crossing
through minimally invasive methods. Clinical decisions due to its anatomical approach while also avoiding the
regarding the vascular access approach are customized to need for cardiopulmonary bypass and sternotomy. 29
individual patient anatomy and comorbidities, and where A major drawback of the TA approach is its relatively
feasible, transfemoral (TF) access is preferred as the least invasive nature, leading to myocardial damage post-
risky approach. The percutaneous puncture and suture procedure, as demonstrated by apical hypokinesis. Al-Hijji
26
pre-closure methods are the preferred approaches for TF et al. emphasized the reduced efficacy of LVEF following
access, with the recommended entry point located between the TA approach compared with the TF method; therefore,
the inferior epigastric artery and femoral bifurcation. 27 this approach is less preferred in patients with cLFLGAS. 30
However, although TF is the preferred option for
TAVR, it may not be feasible in approximately one- 5.2. Prosthetic valves in TAVR
third of the cases due to inadequate iliofemoral vessel With the advancement of TAVR techniques and
dimensions, complex vessel anatomy, or substantial indications, the design of valves has also evolved. Successive
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/bh.4017