Page 31 - BH-3-1
P. 31
Brain & Heart Cardioneuroablation for VMB
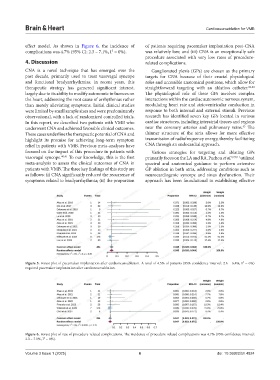
effect model. As shown in Figure 6, the incidence of of patients requiring pacemaker implantation post-CNA
complications was 4.7% (95% CI: 2.3 – 7.1%, I² = 0%). was relatively low; and (iii) CNA is an exceptionally safe
procedure associated with very low rates of procedure-
4. Discussion related complications.
CNA is a novel technique that has emerged over the Ganglionated plexis (GPs) are chosen as the primary
past decade, primarily used to treat vasovagal syncope targets for CNA because of their crucial physiological
and functional bradyarrhythmias. In recent years, this roles and accessible anatomical positions, which allow for
therapeutic strategy has garnered significant interest, straightforward targeting with an ablation catheter. 42-44
largely due to its ability to modify autonomic influences on The physiological role of these GPs involves complex
the heart, addressing the root cause of arrhythmias rather interactions within the cardiac autonomic nervous system,
than merely alleviating symptoms. Initial clinical studies modulating heart rate and atrioventricular conduction in
were limited by small sample sizes and were predominantly response to both internal and external stimuli. Previous
observational, with a lack of randomized controlled trials. research has identified seven key GPs located in various
In this report, we described two patients with VMB who cardiac structures, including interatrial tissues and regions
45
underwent CNA and achieved favorable clinical outcomes. near the coronary arteries and pulmonary veins. The
These cases underline the therapeutic potential of CNA and thinner structure of the atria allows for more effective
highlight its promise for achieving long-term symptom transmission of radiofrequency energy, thereby facilitating
relief in patients with VMB. Previous meta-analyses have CNA through an endocardial approach.
focused on the impact of this procedure in patients with Various strategies for targeting and ablating GPs
vasovagal syncope. 40,41 To our knowledge, this is the first primarily focus on the LA and RA. Pachon et al. 6,7,9,11 utilized
meta-analysis to assess the clinical outcomes of CNA in spectral and anatomical guidance to perform extensive
patients with VMB. The three key findings of this study are GP ablation in both atria, addressing conditions such as
as follows: (i) CNA significantly reduced the recurrence of neurocardiogenic syncope and sinus dysfunction. Their
symptoms related to bradyarrhythmia; (ii) the proportion approach has been foundational in establishing effective
Figure 5. Forest plot of pacemaker implantation after cardioneuroablation. A total of 4.5% of patients (95% confidence interval: 2.6 – 6.4%, I² = 6%)
required pacemaker implantation after cardioneuroablation.
Figure 6. Forest plot of rate of procedure-related complications. The incidence of procedure-related complications was 4.7% (95% confidence interval:
2.3 – 7.1%, I² = 0%).
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/bh.4824