Page 62 - BH-3-1
P. 62
Brain & Heart Thrombectomy for stroke after cardiac surgery
form of post-operative stroke; however, hemorrhagic
stroke due to antithrombotic drugs may also occur.
3
Post-operative stroke may be fatal when it involves large
vessel occlusion (LVO).
Chen et al. conducted a retrospective, nationwide,
2
population-based study of patients with stroke after
coronary and valve surgery and found that all patients
who received surgical treatment for ischemic stroke
underwent decompressive craniectomy. The outcome
was unsatisfactory, with an in-hospital mortality rate
of 12.5% and 1-year mortality rate of 50%. Intravenous
thrombolysis (IVT) is usually contraindicated in these
situations because of the risk of bleeding associated with
recent surgery. Furthermore, IVT may be less effective in
patients with proximal occlusions of the major intracranial
arteries. Therefore, other treatments are urgently needed
4
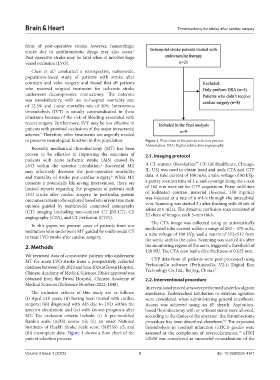
to preserve neurological function in this population. Figure 1. Flow chart of the patient selection process
Abbreviation: DSA: Digital subtraction angiography.
Recently, mechanical thrombectomy (MT) has been
proven to be effective in improving the outcomes of 2.1. Imaging protocol
patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) caused by
™
5
LVO within the anterior circulation. Successful MT A CT scanner (Revolution CT; GE Healthcare, Chicago,
may effectively decrease the post-operative morbidity IL, US) was used to obtain head and neck CTA and CTP
and mortality of stroke post‐cardiac surgery. While MT data. A tube current of 100 mAs, a tube voltage of 80 kVp,
6
presents a potentially life-saving intervention, there are a gantry rotation time of 1 s, and coverage along the z-axis
limited reports regarding the prognosis of patients with of 160 mm were set for CTP acquisition. Forty milliliters
LVO stroke after cardiac surgery. In particular, patient of iodinated contrast material (Ioversol, 350 mg/mL)
outcomes remain to be explored based on current treatment was injected at a rate of 6 mL/s through the antecubital
options guided by multimodal computed tomography vein. Scanning was started 5 s after flushing with 40 mL of
(CT) imaging (including non-contrast CT [NCCT], CT saline at 6 mL/s. The dynamic perfusion scan consisted of
angiography [CTA], and CT perfusion [CTP]). 32 slices of images, each 5-mm thick.
The CTA image was collected using an automatically
In this paper, we present cases of patients from our
institution who underwent MT guided by multimodal CT modulated tube current within a range of 260 – 370 mAs,
a tube voltage of 100 kVp, and a matrix of 512×512 from
to treat LVO stroke after cardiac surgery.
the aortic arch to the calva. Scanning was started 4 s after
2. Methods the monitoring region of the aorta triggered a threshold of
120 HU. The CTA scan had a slice thickness of 0.625 mm.
We reviewed data of consecutive patients who underwent
MT for acute LVO stroke from a prospectively collected CTP data from all patients were post-processed using
database between July 2023 and June 2024 at Fuwai Hospital, PerfusionGo software (PerfusionGo, V2.4; Digital Kun
7
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Ethics approval was Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China).
obtained from the Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of 2.2. Interventional procedure
Medical Sciences (Reference Number: 2022-1848).
Interventional procedures were performed under local groin
The inclusion criteria of this study are as follows: anesthesia. Endotracheal intubation or extreme agitation
(i) Aged ≥18 years; (ii) having been treated with cardiac were considered when administering general anesthesia.
surgery; (iii) diagnosed with AIS due to LVO within the Access was achieved using an 8F sheath. Aspiration-
anterior circulation; and (iv) with known prognosis after based thrombectomy with or without stents were allowed,
MT. The exclusion criteria include: (i) A pre-modified according to the choice of the operator. The thrombectomy
Rankin scale (mRS) scores ≥3; (ii) an onset National procedure has been described elsewhere. The expanded
8,9
Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score (NIHSS) ≤5; and thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (eTICI) grades were
(iii) incomplete data. Figure 1 shows a flow chart of the assessed at the completion of revascularization. eTICI
10
patient selection process. ≥2b50 was considered as successful recanalization of the
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 2 doi: 10.36922/bh.4141