Page 89 - BH-3-1
P. 89
Brain & Heart Brain lesions with PROKR2 microduplication
most functional similarities with vascular endothelial time, the infant developed hepatomegaly and progressive
growth factor and stimulates angiogenic signaling biventricular hypertrophy with pulmonary overflow.
and endothelial cell proliferation, whereas PROK2 Initial metabolic blood and urine tests were normal, except
activation promotes vascular fenestration and increases for elevated capillary lactic acid levels, reaching 55 mg%
permeability. The pathogenetic role of PROKR2 in heart (normal <20 mg%). This elevation prompted further
1
and brain diseases has received particular attention, with analyses, including assessments of urinary organic acids,
studies focusing on diabetic cardiomyopathy, congestive plasma amino acids, acylcarnitines, and serum very-
2
heart failure and hypertrophy, interferon activation, long-chain fatty acids, all of which yielded normal results.
3-6
inflammation, apoptosis, viral and bacterial infections, 7-12 Interestingly, electroencephalographic recording showed
and ischemic brain injury. 13,14 Brain and heart damage no evidence of epileptogenic activity.
appear to be closely associated with the upregulation of the
PROKR2 ligand, which can be activated by external factors Brain magnetic resonance imaging (images not
such as viral and bacterial infections, inflammation, shown) revealed diffuse poor myelination and lateral
hypoxia-ischemia, and excitotoxic glutamate. Copy ventricles dilatation. These findings remained unchanged
15
number variants (CNVs) in the 20p12 region have been during a subsequent hospitalization 2 months later for
found to affect various tissues in humans pathologically, heart failure, despite the infant’s severely deteriorated
most notably the heart. Interestingly, deletions of 20p12.3 condition. Neurological examination during this period
were first found in association with Wolff-Parkinson- also remained substantially unchanged. Given the
16
White (WPW) syndrome, including cases in infants. presence of several dysmorphic features, such as forehead
Subsequent studies, however, identified WPW syndrome hypertrichosis, retroflexed ears with an overfolded right
in families carrying microduplications of the same region. 17 ear, and micrognathia, an array comparative genomic
hybridization analysis was performed. The analysis
The infant reported here represents a rare case of revealed a rare 20p12.3 microduplication of 121 kb, the
brain injury potentially attributed to moderate perinatal region encoding the PROKR2 gene. Despite ongoing
hypoxia and, in particular, a 121 kb microduplication treatment, the infant’s clinical condition did not improve,
in the 20p12.3 region involving the PROKR2 gene. and he passed away at 5 months of age. An autopsy was
A possible gain-of-function mechanism associated with performed with parental consent. The general autopsy
mild hypoxia at birth is hypothesized, as WPW syndrome revealed multiple ischemic cardiac areas with diffuse
characterized by abnormal accessory electrical pathway myocyte necrosis. Neuropathologic examination revealed
between the atria and ventricles was excluded through notable findings.
multiple recordings of normal electrocardiograms (ECGs).
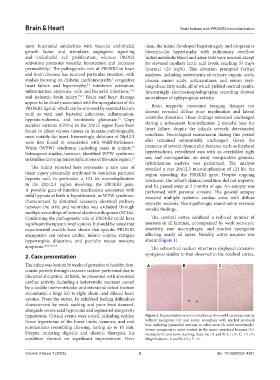
Confirming the pathogenetic role of PROKR2 could have The cerebral cortex exhibited a reduced number of
significant therapeutic implications. It should be noted that neurons in all laminae, accompanied by weak astrocytic
experimental models have shown that specific PROKR2 reactivity, rare macrophages, and marked spongiosis
antagonists can reduce cardiac infarct volume, mitigate affecting nearly all layers. Notably, active necrosis was
hypertrophic dilatation, and partially rescue myocyte absent (Figure 1).
apoptosis. 8,9,15,18,19 The subcortical nuclear structures displayed extensive
2. Case presentation spongiosis similar to that observed in the cerebral cortex,
The infant was born at 36 weeks of gestation to healthy, first- A B C
cousin parents through cesarean section performed due to
placental abruption. At birth, he presented with abnormal
cardiac activity, including a holosystolic murmur caused
by a double interventricular and interatrial defect (ostium
secundum), a large left-to-right shunt, and dilated heart
cavities. From the outset, he exhibited feeding difficulties
characterized by weak sucking and poor food demand,
alongside severe axial hypotonia and segmental antigravity
hypertonus. Critical events were noted, including sudden Figure 1. Representative motor cortical areas show mild neuronal scarcity
flexor hypertonus of the lower limbs, cyanosis, and oral without spongiosis (A) and severe spongiosis with marked neuronal
automatisms resembling chewing, lasting up to 10 min. loss, including pyramidal neurons, in other areas (B, solid arrowheads).
Severe spongiosis is more evident in the more superficial laminae (C).
Despite initiating digitalis and diuretic therapies, his Hematoxylin and eosin staining; Scale bar: A and B: 2.1 cm, C: 1.3 cm;
condition showed no significant improvement. Over Magnifications: A and B: 2.5×, C: 4×.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 2 doi: 10.36922/bh.4281