Page 29 - EER-2-1
P. 29
Explora: Environment
and Resource Evaluating agricultural efficiency and sustainability
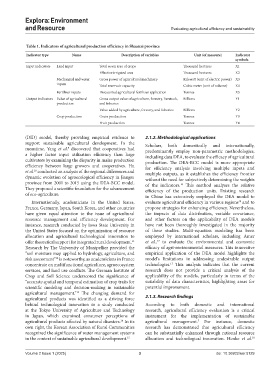
Table 1. Indicators of agricultural production efficiency in Shaanxi province
Indicator type Name Description of variables Unit (of measure) Indicator
symbols
Input indicators Land input Total sown area of crops Thousand hectares X1
Effective irrigated area Thousand hectares X2
Mechanical and water Gross power of agricultural machinery Kilowatt (unit of electric power) X3
inputs Total reservoir capacity Cubic meter (unit of volume) X4
Fertilizer inputs Discounted agricultural fertilizer application Tonnes X5
Output indicators Value of agricultural Gross output value of agriculture, forestry, livestock, Billions Y1
production and fisheries
Value added by agriculture, forestry, and fisheries Billions Y2
Crop production Grain production Tonnes Y3
Fruit production Tonnes Y4
(DID) model, thereby providing empirical evidence to 2.1.2. Methodological applications
support sustainable agricultural development. In the Scholars, both domestically and internationally,
9
meantime, Yang et al. discovered that cooperatives had predominantly employ non-parametric methodologies,
a higher factor input utilization efficiency than large including data DEA, to evaluate the efficacy of agricultural
cultivators by examining the disparity in maize production production. The DEA-BCC model is more appropriate
efficiency between large growers and cooperatives. Hu for efficiency analysis involving multiple inputs and
et al. conducted an analysis of the regional differences and multiple outputs, as it establishes the efficiency frontier
10
dynamic evolution of agroecological efficiency in Jiangsu without the need for subjectively determining the weights
province from 2001 to 2015 using the DEA-BCC model. of the indicators. This method analyses the relative
16
They proposed a scientific foundation for the advancement efficiency of the production units. Existing research
of eco-agriculture. in China has extensively employed the DEA model to
Internationally, academicians in the United States, evaluate agricultural efficiency in various regions and to
10
France, Germany, Japan, South Korea, and other countries propose strategies for enhancing efficiency. Nevertheless,
have given equal attention to the issue of agricultural the impacts of data distribution, variable covariance,
resource management and efficiency development. For and other factors on the applicability of DEA models
instance, research conducted by Iowa State University in have not been thoroughly investigated in the majority
the United States focused on the optimization of resource of these studies. Multi-equation modeling has been
allocation and agricultural technological innovation to employed by international scholars, including Amer
offer theoretical support for integrated rural development. et al., to evaluate the environmental and economic
17
11
Research by The University of Montpellier provided the efficacy of agri-environmental measures. This innovative
“soil moisture map applied to hydrology, agriculture, and empirical application of the DEA model highlights the
risk assessment” is noteworthy, as academicians in France model’s limitations in addressing undesirable output
12
concentrate on multifunctional agriculture, agroecosystem technologies. This analysis indicates that the current
17
services, and land use conflicts. The German Institute of research does not provide a critical analysis of the
Crop and Soil Science underscored the significance of applicability of the models, particularly in terms of the
“accurate spatial and temporal estimation of crop traits for suitability of data characteristics, highlighting areas for
scientific modeling and decision-making in sustainable potential improvement.
agricultural management.” The changing demand for
13
agricultural products was identified as a driving force 2.1.3. Research findings
behind technological innovation in a study conducted According to both domestic and international
at the Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology research, agricultural efficiency evaluation is a critical
in Japan, which examined consumer perceptions of instrument for the implementation of sustainable
agricultural products affected by natural disasters. In its agricultural management. For instance, domestic
14
7
own right, the Korean Association of Rural Communities research has demonstrated that agricultural efficiency
recognized the significance of water management systems can be substantially enhanced through rational resource
in the context of sustainable agricultural development. 15 allocation and technological innovation. Henke et al.
18
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/eer.5129