Page 227 - EJMO-9-1
P. 227
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
Psoas muscle and atherosclerotic inflammation
A B
C
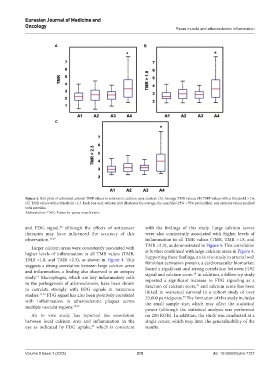
Figure 4. Box plots of estimated arterial TMR values in relation to calcium area clusters. (A) Average TMR values; (B) TMR values with a threshold >1.8;
(C) TMR values with a threshold >2.3. Each box-and-whisker plot illustrates the average, the quartiles (25% – 75% percentiles), and extreme values marked
with asterisks.
Abbreviation: TMR: Tissue-to-psoas muscle ratio.
30
and FDG signal, although the effects of anticancer with the findings of this study. Large calcium scores
therapies may have influenced the accuracy of this were also consistently associated with higher levels of
observation. 16,29 inflammation in all TMR values (TMR, TMR >1.8, and
Larger calcium areas were consistently associated with TMR >2.3), as demonstrated in Figure 5. This correlation
higher levels of inflammation in all TMR values (TMR, is further confirmed with large calcium areas in Figure 4.
Supporting these findings, an in vivo study in arterial wall
TMR >1.8, and TMR >2.3), as shown in Figure 4. This
suggests a strong correlation between large calcium areas fibroblast activation protein, a cardiovascular biomarker,
found a significant and strong correlation between FDG
and inflammation, a finding also observed in an autopsy 38
study. Macrophages, which are key inflammatory cells signal and calcium score. In addition, a follow-up study
31
reported a significant increase in FDG signaling as a
in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, have been shown 39
to correlate strongly with FDG signals in numerous function of calcium score, and calcium score has been
linked to worsened survival in a cohort study of over
studies. 32-34 FDG signal has also been positively correlated 25,000 participants. The limitation of this study includes
40
with inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques across the small sample size, which may affect the statistical
multiple vascular regions. 35,36 power (although the statistical analysis was performed
An in vivo study has reported the association on 200 ROIs). In addition, the study was conducted at a
between local calcium area and inflammation in the single center, which may limit the generalizability of the
37
eye as indicated by FDG uptake, which is consistent results.
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 219 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7727