Page 86 - EJMO-9-1
P. 86
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
T2D polymorphisms in Asians
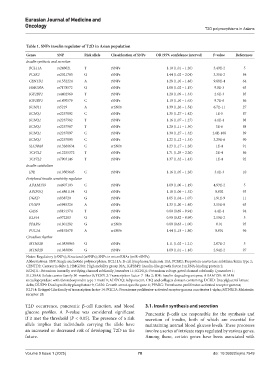
Table 1. SNPs insulin regulator of T2D in Asian population
Genes SNP Risk allele Classification of SNPs OR (95% confidence interval) P‑value References
Insulin synthesis and secretion
BCL11A rs243021 T rSNPs 1.10 (1.01 – 1.20) 3.49E-2 5
PCSK2 rs2021785 G rSNPs 1.44 (1.02 – 2.04) 3.35E-2 84
CENTD2 rs1552224 A rSNPs 1.28 (1.10 – 1.48) 9.88E-4 64
HMG20A rs7178572 G rSNPs 1.08 (1.02 – 1.15) 9.8E-3 63
IGF2BP2 rs4402960 T rSNPs 1.20 (1.09 – 1.33) 2.6E-3 85
IGF2BP2 rs1470579 C rSNPs 1.19 (1.10 – 1.63) 9.7E-6 86
KCNJ11 rs5219 A srSNPs 1.39 (1.26 – 1.54) 6.7E-11 27
KCNQ1 rs2237892 C rSNPs 1.35 (1.27 – 1.42) 1E-5 87
KCNQ1 rs2237982 T rSNPs 1.16 (1.07 – 1.27) 4.1E-4 88
KCNQ1 rs2237987 T rSNPs 1.20 (1.11 – 1.30) 3E-6 88
KCNQ1 rs2237897 C rSNPs 1.30 (1.27 – 1.32) 2.6E-168 89
KCNQ1 rs2237895 C rSNPs 1.22 (1.12 – 1.33) 3.29E-6 90
SLC30A8 rs13266634 C srSNPs 1.23 (1.17 – 1.28) 1E-4 91
TCF7L2 rs12255372 T rSNPs 1.71 (1.29 – 2.26) 2E-4 86
TCF7L2 rs7903146 T rSNPs 1.37 (1.32 – 1.43) 1E-4 92
Insulin catabolism
IDE rs10509645 C rSNPs 1.16 (1.05 – 1.28) 3.1E-3 10
Peripheral insulin sensitivity regulator
ADAMTS9 rs4607103 C rSNPs 1.09 (1.00 – 1.19) 4.93E-2 5
ADIPOQ rs16861194 G rSNPs 1.18 (1.06 – 1.32) 0.002 93
DGKD rs838720 G rSNPs 1.05 (1.04 – 1.07) 1.91E-9 11
DUSP9 rs5945326 A rSNPs 1.33 (1.20 – 1.48) 3.55E-8 63
GAS6 rs8191974 T rSNPs 0.80 (0.69 – 0.94) 4.4E-4 94
KLF14 rs972283 G rSNPs 0.90 (0.82 – 0.99) 2.59E-2 5
PPARG rs1801282 G srSNPs 0.80 (0.63 – 1.00) 0.01 95
PGC1A rs8192678 A srSNPs 1.44 (1.18 – 1.86) 0.001 96
Circadian rhythm
MTNRIB rs10830963 G rSNPs 1.11 (1.02 – 1.21) 2.07E-2 5
MTNRIB rs1083096 G rSNPs 1.09 (1.01 – 1.18) 2.94E-2 97
Notes: Regulatory (rSNPs); Structural (srSNPs); SNPs in microRNAs (miR-rSNPs).
Abbreviations: SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; BCL11A: B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A; PCSK2: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 2;
CENTD2: Centaurin delta 2; HMG20A: High mobility group 20A; IGF2BP2: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2;
KCNJ11: Potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 11; KCNQ1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1;
SLC30A8: Solute carrier family 30-member 8; TCF7L2: Transcription factor-7–like 2; IDE: Insulin-degrading enzyme; ADAMTS9: ADAM
metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 9; ADIPOQ: Adiponectin, C1Q and collagen domain containing; DGKD: Diacylglycerol kinase
delta; DUSP9: Dual specificity phosphatase 9; GAS6: Growth arrest-specific gene 6; PPARG: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma;
KLF14: Krüppel-Like family of transcription factor-14: PGC1A: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; MTNR1B: Melatonin
receptor 1B.
T2D occurrence, pancreatic β-cell function, and blood 3.1. Insulin synthesis and secretion
glucose profiles. A P-value was considered significant Pancreatic β-cells are responsible for the synthesis and
if it met the threshold (P < 0.05). The presence of a risk secretion of insulin, both of which are essential for
allele implies that individuals carrying the allele have maintaining normal blood glucose levels. These processes
an increased or decreased risk of developing T2D in the involve a series of intricate steps regulated by various genes.
future. Among these, certain genes have been associated with
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 78 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7549