Page 87 - EJMO-9-1
P. 87
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
T2D polymorphisms in Asians
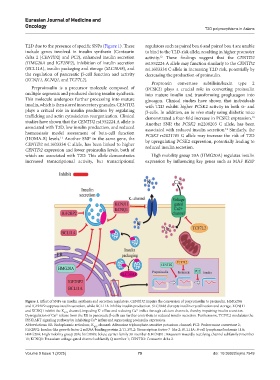
T2D due to the presence of specific SNPs (Figure 1). These regulators such as paired box 6 and paired box 4 are unable
include genes involved in insulin synthesis (Centaurin to bind to the T2D-risk allele, resulting in higher promoter
delta 2 [CENTD2] and PC2), enhanced insulin secretion activity. These findings suggest that the CENTD2
12
(HMG20A and IGF2BP2), inhibition of insulin secretion rs1552224 A allele may function similarly to the CENTD2
(BCL11A), insulin packaging and storage (SLC30A8), and rs11603334 C allele in increasing T2D risk, potentially by
the regulation of pancreatic β-cell function and activity decreasing the production of proinsulin.
(KCNJ11, KCNQ1, and TCF7L2).
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 2
Preproinsulin is a precursor molecule composed of (PCSK2) plays a crucial role in converting proinsulin
multiple segments and produced during insulin synthesis. into mature insulin and transforming proglucagon into
This molecule undergoes further processing into mature glucagon. Clinical studies have shown that individuals
insulin, which is then stored in secretory granules. CENTD2 with T2D exhibit higher PCSK2 activity in both α- and
plays a critical role in insulin production by regulating β-cells. In addition, an in vivo study using diabetic mice
trafficking and actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Clinical demonstrated a four-fold increase in PCSK2 expression.
13
studies have shown that the CENTD2 rs1552224 A allele is Another SNP, the PCSK2 rs2208203 C allele, has been
associated with T2D, low insulin production, and reduced associated with reduced insulin secretion. Similarly, the
14
homeostasis model assessment of beta-cell function PCSK2 rs2021785 G allele may increase the risk of T2D
(HOMA-B) levels. Another SNP in the same gene, the by upregulating PCSK2 expression, potentially leading to
11
CENTD2 rs11603334 C allele, has been linked to higher reduced insulin secretion.
CENTD2 expression and lower proinsulin levels, both of
which are associated with T2D. This allele demonstrates High mobility group 20A (HMG20A) regulates insulin
increased transcriptional activity, but transcriptional expression by influencing key genes such as MAF BZIP
Figure 1. Effect of SNPs on insulin synthesis and secretion regulators. CENTD2 impairs the conversion of preproinsulin to proinsulin. HMG20A
and IGF2BP2 suppress insulin secretion, while BCL11A inhibits insulin production. SLC30A8 disrupts insulin crystallization and storage. KCNJ11
and KCNQ1 inhibit the K ATP channel, impeding K efflux and reducing Ca influx through calcium channels, thereby impairing insulin secretion.
2+
+
Dysregulation of Ca release from the ER in pancreatic β-cells can further contribute to reduced insulin secretion. Furthermore, TCF7L2 modulates the
2+
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by inhibiting Ca influx and suppressing proinsulin expression.
2+
Abbreviations: ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; K ATP channel: Adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel; PC2: Prohormone convertase 2;
IGF2BP2: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2; TCF7L2: Transcription factor-7–like 2; BCL11A: B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A;
HMG20A: High mobility group 20A; SLC30A8: Solute carrier family 30-member 8; KCNJ11: Potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member
11; KCNQ1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1; CENTD2: Centaurin delta 2.
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 79 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7549