Page 92 - EJMO-9-1
P. 92
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
T2D polymorphisms in Asians
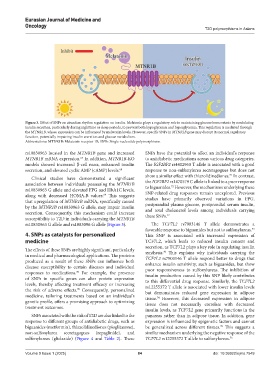
Figure 3. Effect of SNPs on circadian rhythm regulation on insulin. Melatonin plays a regulatory role in maintaining glucose homeostasis by modulating
insulin secretion, particularly during nighttime or sleep periods, to prevent both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. This regulation is mediated through
the MTNR1B, whose expression can be influenced by melatonin levels. However, specific SNPs in MTNR1B gene may disrupt its normal regulatory
function, potentially impairing insulin secretion and glucose metabolism.
Abbreviations: MTNR1B: Melatonin receptor 1B; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms.
rs10830963 located in the MTNR1B gene and increased SNPs have the potential to affect an individual’s response
67
MTNR1B mRNA expression. In addition, MTNR1B-KO to antidiabetic medications across various drug categories.
models showed increased β-cell mass, enhanced insulin The IGF2BP2 rs4402960 T allele is associated with a good
secretion, and elevated cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels. 68 response to non-sulfonylurea secretagogues but does not
71
Clinical studies have demonstrated a significant show a similar effect with thiazolidinediones. In contrast,
association between individuals possessing the MTNR1B the IGF2BP2 rs1470579 C allele is linked to a poor response
to biguanides. However, the mechanisms underlying these
72
rs10830963 G allele and elevated FPG and HbA1C levels,
along with decreased HOMA-B values. This suggests SNP-related drug responses remain unexplored. Previous
69
that upregulation of MTNR1B mRNA, specifically caused studies have primarily observed variations in FPG,
by the MTNR1B rs10830963 G allele, may impair insulin postprandial plasma glucose, postprandial serum insulin,
and total cholesterol levels among individuals carrying
secretion. Consequently, this mechanism could increase these SNPs. 72
susceptibility to T2D in individuals carrying the MTNR1B
rs10830963 G allele and rs1083096 G allele (Figure 3). The TCF7L2 rs7903146 T allele demonstrates a
favorable response to biguanides but not to sulfonylureas.
73
4. SNPs as catalysts for personalized This SNP is associated with increased expression of
medicine TCF7L2, which leads to reduced insulin content and
secretion, as TCF7L2 plays a key role in regulating insulin
The effects of these SNPs are highly significant, particularly synthesis. This explains why individuals carrying the
30
in medical and pharmacological applications. The proteins TCF7L2 rs7903146 T allele respond better to drugs that
produced as a result of these SNPs can influence both enhance insulin sensitivity, such as biguanides, but show
disease susceptibility to certain diseases and individual poor responsiveness to sulfonylureas. The inhibition of
responses to medications. For example, the presence insulin production caused by this SNP likely contributes
70
of SNPs in specific genes can alter protein expression to this differential drug response. Similarly, the TCF7L2
levels, thereby affecting treatment efficacy or increasing rs12255372 T allele is associated with lower insulin levels
the risk of adverse effects. Consequently, personalized but demonstrates reduced gene expression in adipose
70
medicine, tailoring treatments based on an individual’s tissue. However, this decreased expression in adipose
74
genetic profile, offers a promising approach to optimizing tissue does not necessarily correlate with decreased
treatment outcomes. insulin levels, as TCF7L2 gene primarily functions in the
SNPs associated with the risk of T2D are also linked to the pancreas rather than in adipose tissue. In addition, gene
response to different groups of antidiabetic drugs, such as expression is influenced by epigenetic factors and cannot
biguanides (metformin), thiazolidinediones (pioglitazone), be generalized across different tissues. This suggests a
75
non-sulfonylurea secretagogues (repaglinide), and similar mechanism underlying the negative response of the
sulfonylureas (gliclazide) (Figure 4 and Table 2). These TCF7L2 rs12255372 T allele to sulfonylureas. 76
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 84 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7549