Page 90 - EJMO-9-1
P. 90
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
T2D polymorphisms in Asians
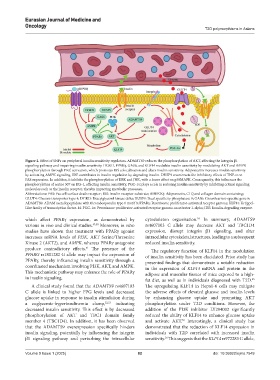
Figure 2. Effect of SNPs on peripheral insulin sensitivity regulators. ADAMTS9 reduces the phosphorylation of AKT, affecting the integrin β1
signaling pathway and impairing insulin sensitivity. DGKD, PPARγ, GAS6, and KLF14 modulate insulin sensitivity by modulating AKT and AMPK
phosphorylation through PKC activation, which promotes IRS colocalization and alters insulin sensitivity. Adiponectin increases insulin sensitivity
by activating AMPK signaling. IDE contributes to insulin regulation by degrading insulin. DUSP9 counteracts the inhibitory effects of TNF-α on
FAS expression. In addition, it inhibits the phosphorylation of ERK and JNK, with a lesser effect on p38MAPK. Consequently, this influences the
phosphorylation of serine 307 on IRS-1, affecting insulin sensitivity. PGC-1α plays a role in reducing insulin sensitivity by inhibiting critical signaling
molecules such as the insulin receptor, thereby impacting metabolic processes.
Abbreviations: FAS: Fas cell surface death receptor; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; ADIPOQ: Adiponectin, C1Q and collagen domain containing;
GLUT4: Glucose transporter type 4; DGKD: Diacylglycerol kinase delta; DUSP9: Dual specificity phosphatase 9; GAS6: Growth arrest-specific gene 6;
ADAMTS9: ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 9; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; KLF14: Krüppel-
Like family of transcription factor-14: PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; IDE: Insulin-degrading enzyme.
54
which affect PPARγ expression, as demonstrated by cytoskeleton organization. In summary, ADAMTS9
various in vivo and clinical studies. 49,50 Moreover, in vitro rs4607103 C allele may decrease AKT and TBC1D4
studies have shown that treatment with PPARγ agonist expression, disrupt integrin β1 signaling, and alter
increases mRNA levels of PI3K, AKT Serine/Threonine intracellular cytoskeletal structures, leading to a subsequent
Kinase 2 (AKT2), and AMPK, whereas PPARγ antagonist reduced insulin sensitivity.
produce contradictory effects. The presence of the The regulatory function of KLF14 in the modulation
51
PPARG rs1801282 G allele may impact the expression of of insulin sensitivity has been elucidated. Prior study has
PPARγ, thereby influencing insulin sensitivity through a presented findings that demonstrate a notable reduction
coordinated mechanism involving PI3K, AKT, and AMPK. in the expression of KLF14 mRNA and protein in the
This mechanistic pathway may enhance the role of PPARγ adipose and muscular tissues of mice exposed to a high-
in insulin signaling. fat diet, as well as in individuals diagnosed with T2D.
55
A clinical study found that the ADAMTS9 rs4607103 The upregulating KLF14 in Hepa1-6 cells may mitigate
C allele is linked to higher FPG levels and decreased the adverse effects of elevated glucose and insulin levels
glucose uptake in response to insulin stimulation during by enhancing glucose uptake and promoting AKT
a euglycemic-hyperinsulinemia clamp, 52,53 indicating phosphorylation under T2D conditions. However, the
decreased insulin sensitivity. This effect is by decreased addition of the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 significantly
phosphorylation of AKT and TBC1 domain family reduced the ability of KLF14 to enhance glucose uptake
55
member 4 (TBC1D4). In addition, it has been observed and activate AKT. Interestingly, a clinical study has
that the ADAMTS9 overexpression specifically hinders demonstrated that the reduction of KLF14 expression in
insulin signaling, potentially by influencing the integrin individuals with T2D correlated with increased insulin
β1 signaling pathway and perturbing the intracellular sensitivity. This suggests that the KLF14 rs972283 G allele,
56
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 82 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7549