Page 112 - EJMO-9-2
P. 112
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology UGVAE of breast lesions
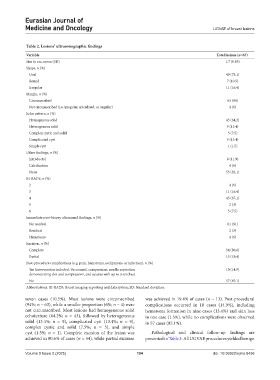
Table 2. Lesions’ ultrasonographic findings
Variable Total lesions (n=67)
Size in cm, mean (SD) 1.7 (0.85)
Shape, n (%)
Oval 49 (73.1)
Round 7 (10.5)
Irregular 11 (16.4)
Margin, n (%)
Circumscribed 63 (94)
Not circumscribed (i.e. irregular, spiculated, or angular) 4 (6)
Echo pattern, n (%)
Homogenous solid 43 (64.2)
Heterogenous solid 9 (13.4)
Complex cystic and solid 5 (7.5)
Complicated cyst 9 (13.4)
Simple cyst 1 (1.5)
Other findings, n (%)
Intraductal 8 (11.9)
Calcification 4 (6)
None 55 (82.1)
BI-RADS, n (%)
2 4 (6)
3 11 (16.4)
4 45 (67.1)
5 2 (3)
6 5 (7.5)
Immediate post-biopsy ultrasound findings, n (%)
No residual 61 (91)
Residual 2 (3)
Hematoma 4 (6)
Excision, n (%)
Complete 54 (80.6)
Partial 13 (19.4)
Post-procedure complications (e.g. pain, hematoma, ecchymosis, or infection), n (%)
Yes (intervention included: Vacuumed, compression, needle aspiration 10 (14.9)
demonstrating clot and compression, and sutures with up to 3 stitches)
No 57 (85.1)
Abbreviations: BI-RADS: Breast imaging-reporting and data system; SD: Standard deviation.
seven cases (10.5%). Most lesions were circumscribed was achieved in 19.4% of cases (n = 13). Post-procedural
(94%; n = 63), while a smaller proportion (6%; n = 4) were complications occurred in 10 cases (14.9%), including
not circumscribed. Most lesions had homogeneous solid hematoma formation in nine cases (13.4%) and skin loss
echotexture (64.2%; n = 43), followed by heterogeneous in one case (1.5%), while no complications were observed
solid (13.4%; n = 9), complicated cyst (13.4%; n = 9), in 57 cases (85.1%).
complex cystic and solid (7.5%; n = 5), and simple
cyst (1.5%; n = 1). Complete excision of the lesion was Pathological and clinical follow-up findings are
achieved in 80.6% of cases (n = 54), while partial excision presented in Table 3. All UGVAE procedures yielded benign
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 104 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8436