Page 192 - EJMO-9-2
P. 192
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Prevalence of PPD in Baghdad
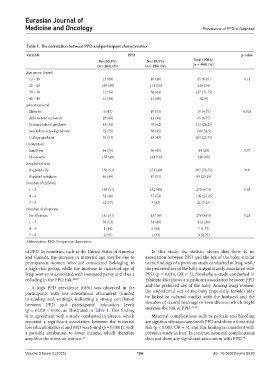
Table 1. The correlation between PPD and participant characteristics
Variable PPD p-value
Yes (50.5%) No (49.5%) Total (100%)
(n = 202) (%) (n = 198) (%) (n = 400) (%)
Age group (years)
12 – 19 15 (60) 10 (40) 25 (6.25) 0.11
20 – 29 105 (49) 111 (51) 216 (54)
30 – 39 71 (56) 56 (44) 127 (31.75)
40 – 49 11 (34) 21 (66) 32 (8)
Education level
Illiterate 9 (47) 10 (53) 19 (4.75) 0.018
Able to read and write 23 (66) 12 (34) 35 (8.75)
Primary school graduate 43 (38) 70 (62) 113 (28.25)
Secondary school graduate 72 (55) 58 (45) 130 (32.5)
College graduate 55 (53) 48 (47) 103 (25.75)
Occupation
Employer 44 (55) 36 (45) 80 (20) 0.37
Housewife 158 (49) 162 (51) 320 (80)
Residential area
Baghdad city 156 (51) 151 (49) 307 (76.75) 0.8
Baghdad outskirts 46 (49) 47 (51) 93 (23.25)
Number of children
1 – 3 138 (51) 132 (49) 270 (67.5) 0.68
4 – 6 52 (48) 57 (52) 109 (27.25
7 – 9 12 (57) 9 (43) 21 (5.25)
Number of abortions
No abortion 141 (51) 137 (49 278 (69.5) 0.25
1 – 3 58 (52) 54 (48) 112 (28)
4 – 6 1 (14) 6 (86) 7 (1.75)
7 – 9 2 (67) 1 (33) 3 (0.75)
Abbreviation: PPD: Postpartum depression.
of PPD. In countries, such as the United States of America In this study, the statistic shows that there is no
and Canada, the increase in maternal age may be due to association between PPD and the sex of the baby, similar
primiparous women who are considered belonging to to the findings of a previous study conducted in Iraq, while
a high-risk group, while the increase in maternal age of the preferred sex of the baby is significantly associated with
Iraqi women is associated with increased parity and thus a PPD (p = 0.014, OR = 2). Similarly, a study conducted in
reducing in the PPD risk. 24,25 Ethiopia also shows a significant association between PPD
A high PPD prevalence (66%) was observed in the and the preferred sex of the baby. Among Iraqi women,
participants with low educational attainment (limited the unpreferred sex of the baby (especially female) may
to reading and writing), indicating a strong correlation be linked to cultural conflict with the husband and the
between PPD and participants’ education levels threaten of second marriage or even divorce, which might
27-29
(p = 0.018 < 0.05), as illustrated in Table 1. This finding increase the risk of PPD.
is in agreement with a study conducted in Greece, which Maternal complications such as pyrexia and bleeding
reported a significant association between the maternal are significantly associated with PPD and show a three-fold
low educational level and PPD was found (p = 0.0001), with risk (p < 0.003, OR = 3), and this finding is consistent with
a possible attribution to lower income, which therefore previous study in Iraq. In contrast, neonatal complications
amplifies the stress on women. 26 does not show any significant association with PPD. 30
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 184 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8528