Page 201 - EJMO-9-2
P. 201
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Vitamin D and HNC: Causal association
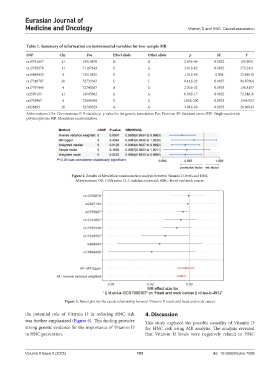
Table 1. Summary of information on instrumental variables for two-sample MR
SNP Chr Pos Effect allele Other allele p SE F
rs10741657 11 14914878 G A 2.05E-46 0.0022 195.9951
rs12785878 11 71167449 T G 3.81E-62 0.0022 272.2431
rs16848425 4 73515825 T C 1.01E-08 0.004 32.48918
rs17216707 20 52732362 C T 8.14E-23 0.0027 94.87964
rs17767445 4 72745267 A G 2.30E-32 0.0033 136.8157
rs2597193 11 14505962 A G 6.26E-17 0.0022 72.24818
rs3755967 4 72609398 T C 1.00E-200 0.0023 1504.053
rs928493 20 52700529 A G 3.98E-08 0.0023 29.06543
Abbreviations: Chr: Chromosome; F: F-statistic; p: p value for the genetic association; Pos: Position; SE: Standard error; SNP: Single-nucleotide
polymorphism; MR: Mendelian randomization.
Figure 2. Results of Mendelian randomization analysis between Vitamin D levels and HNC
Abbreviations: OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; HNC: Head-and-neck cancer.
Figure 3. Forest plot for the causal relationship between Vitamin D levels and head-and-neck cancer
the potential role of Vitamin D in reducing HNC risk 4. Discussion
was further emphasized (Figure 6). This finding provides This study explored the possible causality of Vitamin D
strong genetic evidence for the importance of Vitamin D for HNC risk using MR analysis. The analysis revealed
in HNC prevention. that Vitamin D levels were negatively related to HNC
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 193 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7099