Page 54 - EJMO-9-2
P. 54
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology TCM regulates gut microbiota in pediatric MP pneumonia
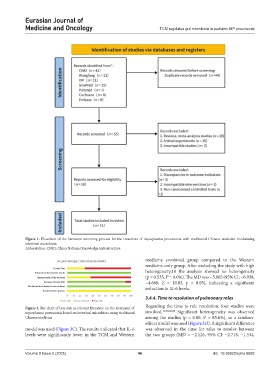
Figure 1. Flowchart of the literature screening process for the treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia with traditional Chinese medicine modulating
intestinal microbiota
Abbreviation: CNKI: China National Knowledge Infrastructure
medicine combined group compared to the Western
medicine-only group. After excluding the study with high
heterogeneity,18 the analysis showed no heterogeneity
(p = 0.535, I = 0.0%). The MD was −5.803 (95% CI: −6.938,
2
−4.668, Z = 10.02, p < 0.05), indicating a significant
reduction in IL-6 levels.
3.4.4. Time to resolution of pulmonary rales
Figure 2. Bar chart of bias risk in relevant literature on the treatment of Regarding the time to rale resolution, four studies were
mycoplasma pneumonia based on intestinal microbiota using traditional involved. 19,20,22,28 Significant heterogeneity was observed
2
Chinese medicine among the studies (p = 0.00, I = 85.6%), so a random-
effects model was used (Figure 3D). A significant difference
model was used (Figure 3C). The results indicated that IL-6 was observed in the time for rales to resolve between
levels were significantly lower in the TCM and Western the two groups (MD = −2.126, 95% CI: −2.718, −1.534,
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 46 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8602