Page 58 - EJMO-9-2
P. 58
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology TCM regulates gut microbiota in pediatric MP pneumonia
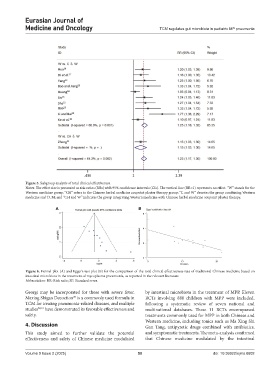
Figure 5. Subgroup analysis of total clinical effectiveness.
Notes: The effect size is presented as risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The vertical line (RR=1) represents no effect. “W” stands for the
Western medicine group; “CH” refers to the Chinese herbal medicine acupoint plaster therapy group; “C and W” denotes the group combining Western
medicine and TCM; and “CH and W” indicates the group integrating Western medicine with Chinese herbal medicine acupoint plaster therapy.
A B
Figure 6. Funnel plot (A) and Egger’s test plot (B) for the comparison of the total clinical effectiveness rate of traditional Chinese medicine based on
intestinal microbiota in the treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia, as reported in the relevant literature
Abbreviation: RR: Risk ratio; SE: Standard error.
Georgi may be incorporated for those with severe fever. by intestinal microbiota in the treatment of MPP. Eleven
Maxing Shigan Decoction is a commonly used formula in RCTs involving 880 children with MPP were included,
29
TCM for treating pneumonia-related diseases, and multiple following a systematic review of seven national and
studies 30,31 have demonstrated its favorable effectiveness and multinational databases. These 11 RCTs encompassed
safety. treatments commonly used for MPP in both Chinese and
Western medicine, including tonics such as Ma Xing Shi
4. Discussion Gan Tang, antipyretic drugs combined with antibiotics,
This study aimed to further validate the potential and symptomatic treatments. The meta-analysis confirmed
effectiveness and safety of Chinese medicine modulated that Chinese medicine modulated by the intestinal
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 50 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8602