Page 57 - EJMO-9-2
P. 57
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology TCM regulates gut microbiota in pediatric MP pneumonia
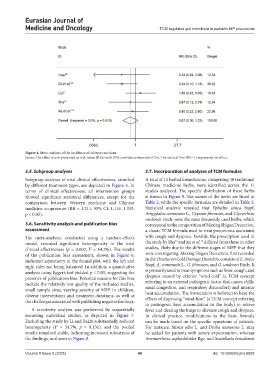
Figure 4. Meta-analysis of the incidence of adverse reactions
Notes: The effect size is presented as risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The vertical line (RR=1) represents no effect.
3.5. Subgroup analyses 3.7. Incorporation of analyses of TCM formulas
Subgroup analyses of total clinical effectiveness, stratified A total of 11 herbal formulations, comprising 40 traditional
by different treatment types, are depicted in Figure 5. In Chinese medicinal herbs, were identified across the 11
terms of clinical effectiveness, all intervention groups studies analyzed. The specific distribution of these herbs
showed significant statistical differences, except for the is shown in Figure 9. The names of the herbs are listed in
comparison between Western medicine and Chinese Table 2, while the specific formulas are detailed in Table 3.
medicine acupressure (RR = 1.211, 95% CI: 1.116, 1.315, Statistical analysis revealed that Ephedra sinica Stapf,
p < 0.05). Amygdalus communis L., Gypsum fibrosum, and Glycyrrhiza
uralensis Fisch. were the most frequently used herbs, which
3.6. Sensitivity analysis and publication bias correspond to the composition of Maxing Shigan Decoction,
assessment a classic TCM formula used to treat pneumonia associated
The meta-analysis, conducted using a random-effects with cough and dyspnea. Notably, the prescription used in
19
22
model, revealed significant heterogeneity in the total the study by Sha and Ke et al. differed from those in other
clinical effectiveness (p = 0.002, I = 64.2%). The results studies, likely due to the different stages of MPP that they
2
of the publication bias assessment, shown in Figure 6, were investigating. Maxing Shigan Decoction, first recorded
indicated asymmetry in the funnel plot, with the left and in the Treatise on Cold Damage Disorders, consists of E. sinica
right sides not being balanced. In addition, a quantitative Stapf, A. communis L., G. fibrosum, and G. uralensis Fisch. It
analysis using Egger’s test yielded p < 0.05, suggesting the is primarily used to treat symptoms such as fever, cough, and
presence of publication bias. Potential reasons for this bias dyspnea caused by exterior “wind-cold” (a TCM concept
include the relatively low quality of the included studies, referring to an external pathogenic factor that causes chills,
small sample sizes, varying severity of MPP in children, nasal congestion, and respiratory discomfort) and interior
diverse interventions and treatment durations, as well as heat accumulation. The formulation is believed to have the
effects of dispersing “wind-heat” (a TCM concept referring
the challenges associated with publishing negative findings.
to pathogenic heat accumulation in the body) to relieve
A sensitivity analysis was performed by sequentially fever and clearing the lungs to alleviate cough and dyspnea.
removing individual studies, as depicted in Figure 7. In clinical practice, modifications to the basic formula
Excluding the study by Li and Bai20 substantially reduced can be made based on the specific symptoms of patients.
heterogeneity (I = 34.7%, p = 0.131), and the pooled For instance, Morus alba L. and Draba nemorosa L. may
2
results remained stable, indicating increased robustness of be added for patients with severe expectoration, whereas
the findings, as shown in Figure 8. Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bge. and Scutellaria baicalensis
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 49 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8602