Page 14 - EJMO-9-3
P. 14
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Progress in the research of pathology and therapy in liver fibrosis
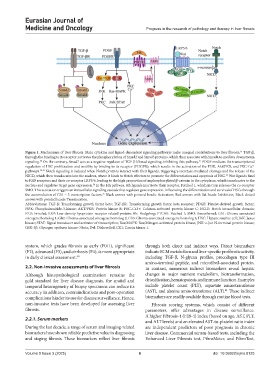
Figure 1. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis. Main cytokine and ligand-dependent signaling pathways make unequal contributions to liver fibrosis. TGF-β,
14
through the binding to its receptor, activates the phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 proteins, which then associate with Smad4 to mediate downstream
signaling. On the contrary, Smad7 acts as a negative regulator of TGF-β1/Smad signaling, inhibiting this pathway. PDGF mediates the transcriptional
30
31
regulation of HSC proliferation and motility by binding to its receptor (PDGFR), which results in the activation of the PI3K, Akt/PKB, and PKC-Ca
2+
pathways. 32,33 Notch signaling is induced when Notch proteins interact with their ligands, triggering γ-secretase-mediated cleavage and the release of the
NICD, which then translocates into the nucleus, where it binds to Notch effectors to promote the differentiation and apoptosis of HSC. Wnt ligands bind
33
to FZD receptors and their co-receptor LRP5/6, leading to the high proportion of unphosphorylated β-catenin in the cytoplasm, which translocates to the
nucleus and regulates target gene expression. In the Hh pathway, Hh ligands inactivate their receptor, Patched 1, which in turn releases the co-receptor
34
SMO. This activation triggers an intracellular signaling cascade that regulates gene expression, influencing the differentiation and survival of HSCs through
the accumulation of Gli1 – 3 transcription factors. Black arrows with pointed heads: Activation; Red arrows with flat heads: Inhibition; Black dotted
35
arrows with pointed heads: Translocation.
Abbreviations: TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; TGF-βR: Transforming growth factor beta receptor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor;
PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3-kinase; AKT/PKB: Protein kinase B; PKC-Ca2+: Calcium-activated protein kinase C; NCID: Notch intracellular domain;
FZD: Frizzled; LRP: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; Hh: Hedgehog; PTCH1: Patched 1; SMO: Smoothened; Gli1: Glioma-associated
oncogene homolog 1; Gli2: Glioma-associated oncogene homolog 2; Gli3: Glioma-associated oncogene homolog 3; HSC: Hepatic satellite cell; JAK: Janus
kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; Ras/MAPK: Ras/Mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase;
GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; Dvl: Dishevelled; CK1: Casein kinase 1.
system, which grades fibrosis as early (F0/1), significant through both direct and indirect ways. Direct biomarkers
(F2), advanced (F3), and cirrhosis (F4), is more appropriate indicate ECM metabolism and liver-specific profibrotic activity,
in daily clinical assessment. 40 including TGF-β, N-glycan profiles, procollagen type III
amino-terminal peptide, and microfibril-associated protein.
2.2. Non-invasive assessments of liver fibrosis In contrast, numerous indirect biomarkers reveal hepatic
Although histopathological examination remains the changes in major nutrient metabolism, biotransformation,
gold standard for liver disease diagnosis, the spatial and detoxification, hematopoiesis, and immune function. Examples
temporal heterogeneity of biopsy specimens can reduce its include platelet count (PLT), aspartate aminotransferase
41
accuracy. In addition, contraindications and post-operation (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT). These indirect
complications hinder its use for disease surveillance. Hence, biomarkers are readily available through routine blood tests.
non-invasive tests have been developed for assessing liver Fibrosis scoring systems, which consist of different
fibrosis. parameters, offer advantages in disease surveillance.
A higher Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index (based on age, AST, PLT,
2.2.1. Serum markers
and ALT levels) and an elevated AST-to-platelet ratio index
During the last decade, a range of serum and imaging-related are independent predictors of poor prognosis in chronic
biomarkers have shown reliable predictive value in diagnosing liver disease. Commercial serum-based tests, including the
and staging fibrosis. These biomarkers reflect liver fibrosis Enhanced Liver Fibrosis test, FibroMeter, and FibroTest,
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8125