Page 170 - EJMO-9-3
P. 170
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Psychological care for cancer patients
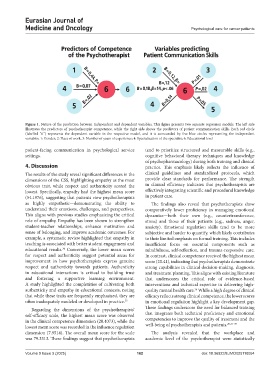
Figure 1. Nature of the prediction between independent and dependent variables. This figure presents two separate regression models. The left side
illustrates the predictors of psychotherapist competence, while the right side shows the predictors of patient communication skills. Each red circle
(labelled “6”) represents the dependent variable in the respective model, and it is surrounded by five blue circles representing the independent
variables: 1: Gender; 2: Place of work, 3: Number of years of experience; 4: Specialization of the specialist; 6: Educational level
patient-facing communication in psychological service tend to prioritize structured and measurable skills (e.g.,
settings. cognitive behavioral therapy techniques and knowledge
of psychopharmacology) during both training and clinical
4. Discussion practice. This emphasis likely reflects the influence of
The results of the study reveal significant differences in the clinical guidelines and standardized protocols, which
dimensions of the CSS, highlighting empathy as the most provide clear standards for performance. The strength
obvious trait, while respect and authenticity scored the in clinical efficiency indicates that psychotherapists are
lowest. Specifically, empathy had the highest mean score effectively integrating scientific and procedural knowledge
(54.1976), suggesting that patients view psychotherapists in patient care.
as highly empathetic—demonstrating the ability to The findings also reveal that psychotherapists show
understand their emotions, challenges, and perspectives. comparatively lower proficiency in managing emotional
This aligns with previous studies emphasizing the critical dynamics—both their own (e.g., countertransference,
role of empathy. Empathy has been shown to strengthen stress) and those of their patients (e.g., sadness, anger,
student-teacher relationships, enhance motivation and anxiety). Emotional regulation skills tend to be more
sense of belonging, and improve academic outcomes. For subjective and harder to quantify, which likely contributes
example, a systematic review highlighted that empathy in to their limited emphasis on formal training. This includes
teaching is associated with better student engagement and insufficient focus on essential components such as
34
educational results. Conversely, the lower mean scores mindfulness, self-reflection, and trauma-responsive care.
for respect and authenticity suggest potential areas for In contrast, clinical competence received the highest mean
improvement in how psychotherapists express genuine score (20.41), indicating that psychotherapists demonstrate
respect and authenticity towards patients. Authenticity strong capabilities in clinical decision-making, diagnosis,
in educational interactions is critical to building trust and treatment planning. This aligns with existing literature
and fostering a supportive learning environment. that underscores the critical role of evidence-based
A study highlighted the complexities of cultivating both interventions and technical expertise in delivering high-
authenticity and empathy in educational contexts, noting quality mental health care. While a high degree of clinical
36
that while these traits are frequently emphasized, they are efficacy reflects strong clinical competence, the lower scores
often inadequately modeled or developed in practice. 35 in emotional regulation highlight a key development gap.
Regarding the dimensions of the psychotherapists’ These findings underscore the need for balanced training
self-efficacy scale, the highest mean score was observed that integrates both technical proficiency and emotional
in the clinical competence dimension (20.4073), while the competencies to improve the quality of treatment and the
20,37-39
lowest mean score was recorded in the influence regulation well-being of psychotherapists and patients.
dimension (7.9514). The overall mean score for the scale The analysis revealed that the workplace and
was 79.3313. These findings suggest that psychotherapists academic level of the psychotherapist were statistically
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 162 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025110054