Page 93 - GHES-2-1
P. 93
Global Health Econ Sustain Job satisfaction and burnout in the catering industry
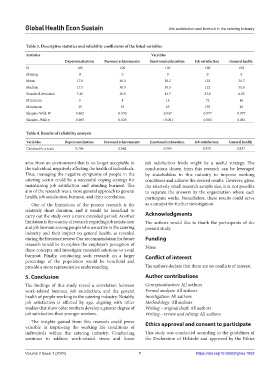
Table 3. Descriptive statistics and reliability coefficients of the listed variables
Statistics Variables
Depersonalization Personal achievements Emotional exhaustion Job satisfaction General health
N 100 100 100 100 100
Missing 0 0 0 0 0
Mean 17.8 36.0 36.2 122 31.7
Median 17.5 38.0 35.5 122 31.0
Standard deviation 7.45 10.5 13.7 23.8 6.23
Minimum 5 8 14 72 16
Maximum 35 55 63 195 45
Shapiro-Wilk W 0.962 0.970 0.947 0.977 0.977
Shapiro–Wilk p 0.005 0.023 < 0.001 0.083 0.081
Table 4. Results of reliability analysis
Variables Depersonalization Personal achievements Emotional exhaustion Job satisfaction General health
Cronbach’s α scale 0.784 0.842 0.903 0.878 0.837
arise from an environment that is no longer acceptable to job satisfaction levels might be a useful strategy. The
the individual, negatively affecting the health of individuals. conclusions drawn from this research can be leveraged
Thus, managing the negative symptoms of people in the by stakeholders in this industry to improve working
catering sector could be a successful coping strategy for conditions and achieve the desired results. However, given
maintaining job satisfaction and avoiding burnout. The the relatively small research sample size, it is not possible
aim of the research was a more general approach to general to separate the answers by the organization where each
health, job satisfaction, burnout, and their correlation. participant works. Nonetheless, these results could serve
One of the limitations of the present research is the as a catalyst for further investigation.
relatively short duration, and it would be beneficial to
carry out the study over a more extended period. Another Acknowledgments
limitation is the scarcity of research regarding job satisfaction The authors would like to thank the participants of the
and job burnout among people who are active in the catering present study.
industry and their impact on general health, as revealed
during the literature review. Our recommendation for future Funding
research would be to explore the employer’s perception of None.
these concepts and investigate potential solutions to avoid
burnout. Finally, conducting such research on a larger Conflict of interest
percentage of the population would be beneficial and
provide a more representative understanding. The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
5. Conclusion Author contributions
The findings of this study reveal a correlation between Conceptualization: All authors
work-related burnout, job satisfaction, and the general Formal analysis: All authors
health of people working in the catering industry. Notably, Investigation: All authors
job satisfaction is affected by age, aligning with other Methodology: All authors
studies that show older workers develop a greater degree of Writing – original draft: All authors
job satisfaction than younger workers. Writing – review and editing: All authors
The insights gained from this research could prove Ethics approval and consent to participate
valuable in improving the working life conditions of
individuals within the catering industry. Conducting This study was conducted according to the guidelines of
seminars to address work-related stress and boost the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1852