Page 146 - GHES-3-1
P. 146
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Reducing public stigma related to psychosis
The ANOVA results for forcing treatment, empathy, values had fewer items and the current study’s sample
social restrictiveness, and prejudice/misconception size was 133, the internal consistency reliability might be
indicated no significant interaction between time and underestimated. Therefore, all subscales were included in
group (p > 0.05). Therefore, the notable effects observed the present study.
from pretest to post-test for these factors were not
maintained at follow-up, and no post hoc analyses were 4. Discussion
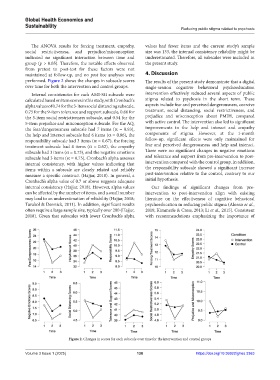
performed. Figure 2 shows the changes in subscale scores The results of the present study demonstrate that a digital
over time for both the intervention and control groups. single-session cognitive behavioral psychoeducation
Internal consistencies for each AMI-SG subscale were intervention effectively reduced several aspects of public
calculated based on item scores in this study, with Cronbach’s stigma related to psychosis in the short term. These
alpha values of 0.74 for the 3-item social distancing subscale, aspects include fear and perceived dangerousness, coercive
0.75 for the 9-item tolerance and support subscale, 0.66 for treatment, social distancing, social restrictiveness, and
the 3-item social restrictiveness subscale, and 0.54 for the prejudice and misconception about PMIH, compared
5-item prejudice and misconception subscale. For the AQ, with active control. The intervention also led to significant
the fear/dangerousness subscale had 7 items (α = 0.93), improvements in the help and interact and empathy
the help and interact subscale had 6 items (α = 0.86), the components of stigma. However, at the 1-month
responsibility subscale had 3 items (α = 0.67), the forcing follow-up, significant effects were only maintained for
treatment subscale had 4 items (α = 0.62), the empathy fear and perceived dangerousness and help and interact.
subscale had 3 items (α = 0.73), and the negative emotions There were no significant changes in negative emotions
subscale had 3 items (α = 0.75). Cronbach’s alpha assesses and tolerance and support from pre-intervention to post-
internal consistency, with higher values indicating that intervention compared with the control group. In addition,
items within a subscale are closely related and reliably the responsibility subscale showed a significant increase
measure a specific construct (Hajjar, 2018). In general, a post-intervention relative to the control, contrary to our
Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.7 or above suggests adequate initial hypothesis.
internal consistency (Hajjar, 2018). However, alpha values Our findings of significant changes from pre-
can be affected by the number of items, and a small number intervention to post-intervention align with existing
may lead to an underestimation of reliability (Hajjar, 2018; literature on the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral
Tavakol & Dennick, 2011). In addition, significant results psychoeducation in reducing public stigma (Alonso et al.,
often require a large sample size, typically over 200 (Hajjar, 2019; Kimmerle & Cress, 2013; Li et al., 2015). Consistent
2018). Given that subscales with lower Cronbach’s alpha with recommendations emphasizing the importance of
Figure 2. Changes in scores for each subscale over time for the intervention and control groups
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 138 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.3363