Page 143 - GHES-3-1
P. 143
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Reducing public stigma related to psychosis
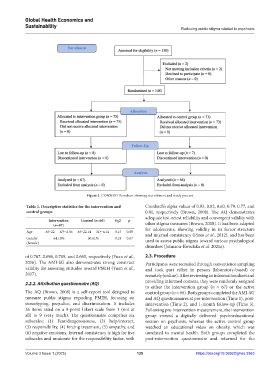
Figure 1. CONSORT flowchart showing recruitment and study process
Table 1. Descriptive statistics for the intervention and Cronbach’s alpha values of 0.93, 0.82, 0.60, 0.79, 0.77, and
control groups 0.81, respectively (Brown, 2008). The AQ demonstrates
adequate test-retest reliability and convergent validity with
Intervention Control (n=66) t/χ2 p
(n=67) other stigma measures (Brown, 2008). It has been adapted
Age M=22 SD=4.56 M=22.14 SD=6.14 0.15 0.89 for adolescents, showing validity in its factor structure
and internal consistency (Pinto et al., 2012), and has been
Gender 64.18% 60.61% 0.18 0.67 used to assess public stigma toward various psychological
(female)
disorders (Johnson-Kwochka et al. 2021a).
of 0.707, 0.696, 0.709, and 0.665, respectively (Yuan et al., 2.3. Procedure
2016). The AMI-SG also demonstrates strong construct Participants were recruited through convenience sampling
validity for assessing attitudes toward PMIH (Yuan et al., and took part either in person (laboratory-based) or
2017). remotely (online). After reviewing an information sheet and
2.2.2. Attribution questionnaire (AQ) providing informed consent, they were randomly assigned
to either the intervention group (n = 67) or the active
The AQ (Brown, 2008) is a self-report tool designed to control group (n = 66). Both groups completed the AMI-SG
measure public stigma regarding PMIH, focusing on and AQ questionnaires at pre-intervention (Time 1), post-
stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination. It includes intervention (Time 2), and 1-month follow-up (Time 3).
26 items rated on a 9-point Likert scale from 1 (not at Following pre-intervention measurement, the intervention
all) to 9 (very much). The questionnaire comprises six group viewed a digitally delivered psychoeducational
subscales: (1) Fear/dangerousness, (2) help/interact, session on psychosis, whereas the active control group
(3) responsibility, (4) forcing treatment, (5) empathy, and watched an educational video on obesity, which was
(6) negative emotions. Internal consistency is high for five unrelated to mental health. Both groups completed the
subscales and moderate for the responsibility factor, with post-intervention questionnaire and returned for the
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 135 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.3363