Page 161 - GHES-3-1
P. 161
Global Health Economics and
Sustainability
Affect heuristics in substance use
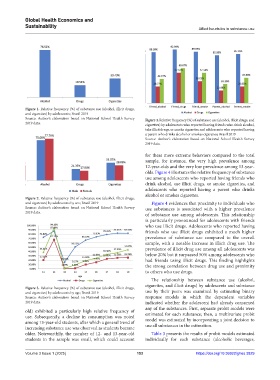
Figure 1. Relative frequency (%) of substance use (alcohol, illicit drugs,
and cigarettes) by adolescents; Brazil 2019
Source: Author’s elaboration based on National School Health Survey Figure 4. Relative frequency (%) of substance use (alcohol, illicit drugs, and
2019 data. cigarettes) by adolescents who reported having friends who drink alcohol,
take illicit drugs, or smoke cigarettes and adolescents who reported having
a parent who drinks alcohol or smokes cigarettes; Brazil 2019
Source: Author’s elaboration based on National School Health Survey
2019 data.
for these more extreme behaviors compared to the total
sample, for instance, the very high prevalence among
12-year-olds and the very low prevalence among 13-year-
olds. Figure 4 illustrates the relative frequency of substance
use among adolescents who reported having friends who
drink alcohol, use illicit drugs, or smoke cigarettes, and
adolescents who reported having a parent who drinks
alcohol or smokes cigarettes.
Figure 2. Relative frequency (%) of substance use (alcohol, illicit drugs,
and cigarettes) by adolescents by sex; Brazil 2019 Figure 4 evidences that proximity to individuals who
Source: Author’s elaboration based on National School Health Survey use substances is associated with a higher prevalence
2019 data.
of substance use among adolescents. This relationship
is particularly pronounced for adolescents with friends
who use illicit drugs. Adolescents who reported having
friends who use illicit drugs exhibited a much higher
prevalence of substance use compared to the overall
sample, with a notable increase in illicit drug use. The
prevalence of illicit drug use among all adolescents was
below 20% but it surpassed 50% among adolescents who
had friends using illicit drugs. This finding highlights
the strong correlation between drug use and proximity
to others who use drugs.
The relationship between substance use (alcohol,
cigarettes, and illicit drugs) by adolescents and substance
Figure 3. Relative frequency (%) of substance use (alcohol, illicit drugs,
and cigarettes) by adolescents by age; Brazil 2019 use by their peers was examined by estimating binary
Source: Author’s elaboration based on National School Health Survey response models in which the dependent variables
2019 data. indicated whether the adolescent had already consumed
any of the substances. First, separate probit models were
old) exhibited a particularly high relative frequency of
use. Subsequently, a decline in consumption was noted estimated for each substance; then, a multivariate probit
among 13-year-old students, after which a general trend of model was estimated by incorporating a joint decision to
increasing substance use was observed as students became use all substances in the estimation.
older. Noteworthily, the number of 12- and 13-year-old Table 3 presents the results of probit models estimated
students in the sample was small, which could account individually for each substance (alcoholic beverages,
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 153 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.3829