Page 36 - GPD-1-2
P. 36
Gene & Protein in Disease RUNX1 gene in female-related cancers
cells, indicating that RUNX1 is essential for healthy cell
proliferation, and sustaining the pivotal role of RUNX1 in
the mammary gland.
4. Impact of RUNX1 mutation
Chromosomal translocations are a specific type of mutation,
in which abnormal exchanges occur between homologous
chromosomes. According to numerous studies related to
different forms of cancers, the RUNX1 locus is a common
site for multiple chromosomal translocations. Monoallelic
point mutations such as the one that results in the loss of
RUNX1-MTG16 contribute to breast cancer.
RUNX1-MTG16 protein is the result of a fusion
between the RUNX1 at its N terminus (truncated at
the runt domain) to the C terminus of MTG16 protein
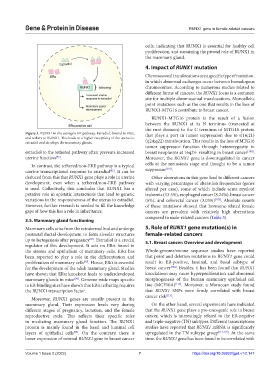
Figure 3. RUNX1 in the estrogen-ER pathway. Estradiol, bound to ERα, that plays a part in tumor suppression due to t(16;21)
and tethers to RUNX1. This leads to a higher receptivity of the uterus to
estradiol and develops the mammary glands. (q24;q22) translocation. This results in the loss of MTG16
tumor suppressor function through heterozygosity in
estradiol to the tethered pathway often prevents increased breast neoplasms at 16q24- resulting in breast cancer [100] .
uterine function . Moreover, the RUNX1 gene is downregulated in cancer
[95]
In contrast, the tethered/non-ERE pathway is a typical cells at the metastasis stage and thought to be a tumor
uterine transcriptional response to estradiol . It can be suppressor [101] .
[95]
deduced from this that RUNX1 gene plays a role in uterine Other aberrations in this gene lead to different cancers
development, even when a tethered/non-ERE pathway with varying percentages of alteration frequencies (genes
is used. Collectively, this concludes that RUNX1 has a altered per case), some of which include acute myeloid
putative role in epistatic interactions that lead to genetic leukemia (13.5%), esophageal cancer (8.24%), breast cancer
variations in the responsiveness of the uterus to estradiol. (6%), and colorectal cancer (3.03%) [102] . Absolute counts
However, further research is needed to fill the knowledge of these mutations showed that hormone-related female
gaps of how this has a role in inheritance. cancers are prevalent with relatively high aberrations
compared to male-related cancers (Table 3).
3.5. Mammary gland functioning
Mammary cells arise from the ectodermal bud and undergo 5. Role of RUNX1 gene mutation(s) in
postnatal ductal development to form alveolar structures female-related cancers
up to lactogenesis after pregnancy . Estradiol is a crucial 5.1. Breast cancer: Overview and development
[96]
regulator of this development. It acts on ERα found in
the stroma and epithelium of mammary cells. ERα has Whole-genome/exome sequence studies have reported
been reported to play a role in the differentiation and that point and deletion mutations in RUNX1 gene could
proliferation of mammary cells . Hence, ERα is essential result in ER-positive, luminal, and basal subtype of
[97]
for the development of the adult mammary gland. Studies breast cancer [104] . Besides, it has been found that RUNX1
have shown that ERα knockout leads to underdeveloped knockdown may cause hyperproliferation and abnormal
mammary glands in mice . Genome-wide maps specific morphogenesis of the human mammary epithelial cell
[98]
to ER-binding sites have shown that ERα tethering requires line (MCF10A) [112] . Moreover, a Moroccan study found
the RUNX1 transcription factor. that RUNX1 SNPs were firmly correlated with breast
cancer risk [113] .
Moreover, RUNX1 genes are usually present in the
mammary gland. Their expression levels vary during On the other hand, several experiments have indicated
different stages of pregnancy, lactation, and the female that the RUNX1 gene plays a pro-oncogenic role in breast
reproductive cycle. This reflects their specific roles cancer, which is interestingly related to the ER-negative
in mediating mammary gland function. The RUNX1 and triple-negative (TN) subtypes. Different transcriptome
protein is mainly found in the basal and luminal cell studies have reported that RUNX1 mRNA is significantly
layers of epithelial cells . On the contrary, there is upregulated in the TN subtype group [114,115] . At the same
[99]
lower expression of normal RUNX1 gene in breast cancer time, the RUNX1 gene has been found to be correlated with
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.147