Page 38 - GPD-1-2
P. 38
Gene & Protein in Disease RUNX1 gene in female-related cancers
factor, whose expression also seemed to be upregulated gene expression increased the rate of metastasis in an
during the primary steps of EEC progression. Moreover, orthotropic endometrial mouse model, implicating the
high levels of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and ‐9 gene as a putative inducer of metastasis [105] . Therefore,
expression have also been found to colocalize with ERM/ RUNX1 is a pro-oncogenic player in uterine cancer. The
ETV5 and RUNX1 at the invasive front of endometrial mutations observed in RUNX1 gene are mostly due to
cells, encouraging an interplay between these proteins myometrial infiltration, substitution, mRNA upregulation,
during myometrial infiltration [120,121] . Besides, the RUNX1 or in very few cases, heterozygous point mutations [107] .
gene is also strongly associated with the expression of EEC, or type I endometrioid endometrial carcinoma, is
the double‐strand‐break repair protein rad21 homolog one of the two types of uterine cancer, in which the gene
(RAD21), a crucial component of the cohesin complex expression profile of RUNX1 has the highest value.
that is involved in chromosome segregation and often
dysregulated in solid tumors of the breast and ovary [122,123] . 5.3. Ovarian cancer: Overview and development
Surprisingly, experiments in zebrafish have revealed that Of all the female gynecological malignancies, ovarian
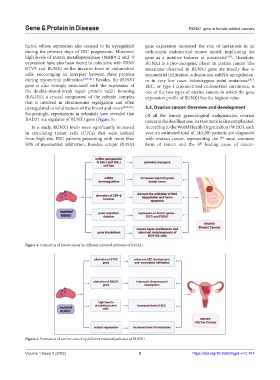
RAD21 is a regulator of RUNX1 gene (Figure 5). cancer is the deadliest one. Its treatment is also complicated.
In a study, RUNX1 levels were significantly increased According to the World Health Organization (WHO), each
in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) that were isolated year, an estimated total of 140,200 patients are diagnosed
th
from high‐risk EEC patients presenting with more than with ovarian cancer, representing the 7 most common
50% of myometrial infiltration. Besides, ectopic RUNX1 form of cancer and the 8 leading cause of cancer-
th
Figure 4. Formation of breast cancer by different mutated pathways of RUNX1.
Figure 5. Formation of uterine cancer by different mutated pathways of RUNX1.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.147