Page 37 - GPD-1-2
P. 37
Gene & Protein in Disease RUNX1 gene in female-related cancers
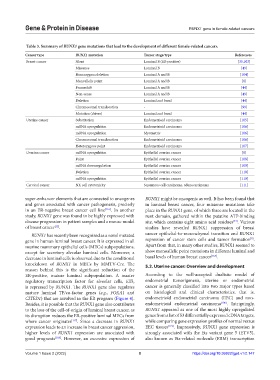
Table 3. Summary of RUNX1 gene mutations that lead to the development of different female‑related cancers.
Cancer type RUNX1 mutation Tumor stage/type References
Breast cancer Silent Luminal B (ER-positive) [35,103]
Missense Luminal B [49]
Homozygous deletion Luminal A and B [104]
Monoallelic point Luminal A and B [8]
Frameshift Luminal A and B [44]
Non-sense Luminal A and B [49]
Deletion Luminal and basal [44]
Chromosomal translocation - [99]
Mutation (driver) Luminal and basal [44]
Uterine cancer Substitution Endometrioid carcinoma [105]
mRNA upregulation Endometrioid carcinoma [106]
mRNA upregulation Myometric [106]
Chromosomal translocation Endometrioid carcinoma [106]
Heterozygous point Endometrioid carcinoma [107]
Ovarian cancer mRNA upregulation Epithelial ovarian cancer [8]
Point Epithelial ovarian cancer [108]
mRNA downregulation Epithelial ovarian cancer [109]
Deletion Epithelial ovarian cancer [110]
mRNA upregulation Epithelial ovarian cancer [110]
Cervical cancer NK cell cytotoxicity Squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma [111]
super‐enhancer elements that are connected to oncogenes RUNX1 might be oncogenic as well. It has been found that
and genes associated with cancer pathogenesis, precisely in luminal breast cancer, four missense mutations take
in an ER-negative breast cancer cell line [116] . In another place in the RUNX1 gene, of which three are located in the
study, RUNX1 gene was found to be highly expressed with runt domain, gathered within the putative ATP-binding
disease progression in patient samples and a mouse model site, which contains eight amino acid residues . Various
[44]
of breast cancer . studies have revealed RUNX1 suppression of breast
[35]
RUNX1 has recently been recognized as a novel mutated cancer epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and RUNX1
[8]
gene in human luminal breast cancer. It is expressed in all repression of cancer stem cells and tumor formation .
murine mammary epithelial cells (MECs) subpopulations, Apart from that, in many other studies, RUNX1 seemed to
except for secretory alveolar luminal cells. Moreover, a show monoallelic point mutations in different luminal and
decrease in luminal cells is observed due to the conditional basal levels of human breast cancer [118] .
knockdown of RUNX1 in MECs by MMTV-Cre. The 5.2. Uterine cancer: Overview and development
reason behind this is the significant reduction of the
ER-positive, mature luminal subpopulation. A master According to the well‐accepted dualistic model of
regulatory transcription factor for alveolar cells, Elf5, endometrial tumorigenesis, uterine or endometrial
is repressed by RUNX1. The RUNX1 gene also regulates cancer is generally classified into two major types based
mature luminal TF/co-factor genes (e.g., FOXA1 and on histological and clinical characteristics, that is,
CITED1) that are involved in the ER program (Figure 4). endometrioid endometrial carcinoma (EEC) and non-
Besides, it is possible that the RUNX1 gene also contributes endometrioid endometrial carcinoma [106] . Intriguingly,
to the loss of the cell-of-origin of luminal breast cancer, as RUNX1 appeared as one of the most highly upregulated
its disruption reduces the ER-positive luminal MECs from genes from a list of 53 differentially expressed cDNA targets,
where cancer originates [117] . Since a decrease in RUNX1 while comparing gene expression profiles of normal versus
expression leads to an increase in breast cancer aggression, EEC tissues [119] . Impressively, RUNX1 gene expression is
higher levels of RUNX1 expression are associated with strongly associated with the Ets variant gene 5 (ETV5),
good prognosis [103] . However, an excessive expression of also known as Ets-related molecule (ERM) transcription
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.147