Page 69 - GPD-2-3
P. 69
Gene & Protein in Disease Testosterone as a biomarker of colorectal cancer
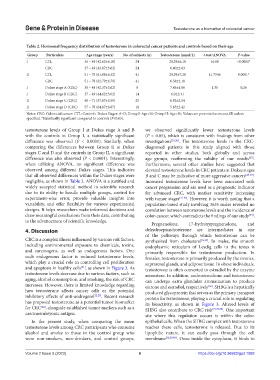
Table 2. Hormonal frequency distribution of testosterone in colorectal cancer patients and controls based on their age
Group Particulars Age range (years) No. of subjects (n) Testosterone (nmol/L) t‑test/ANOVA P‑value
I CTL 36 – 49 (42.62±6.10) 24 28.29±6.10 16.68 <0.0001*
CRC 37 – 49 (43.87±3.62) 24 6.40±2.03
II CTL 51 – 75 (61.08±6.32) 41 20.39±7.20 11.7546 0.0001*
CRC 51 – 78 (62.79±6.79) 41 6.58±2.18
I Dukes stage A (CRC) 38 – 48 (42.37±3.62) 8 7.43±1.86 1.35 0.26
I Dukes stage B (CRC) 37 – 49 (44.62±3.02) 14 6.0±2.31
II Dukes stage C (CRC) 48 – 71 (57.87±5.59) 25 6.92±2.54
II Dukes stage D (CRC) 57 – 78 (64.87±6.87) 18 5.85±2.42
Notes: CRC: Colorectal cancer: CTL: Controls. Dukes Stages: A–D; Group I: Age<50; Group II: Age>50; Values are presented as mean±SD unless
specified. *Statistically significant compared to controls (P<0.05).
testosterone levels of Group I at Dukes stage A and B we observed significantly lower testosterone levels
with the controls in Group I, a statistically significant (P < 0.05), which is consistent with findings from other
difference was observed (P < 0.0001). Similarly, when investigations [25,26] . The testosterone levels in the CRC-
comparing the differences between Group II at Dukes diagnosed patients in this study aligned with those
stages C and D and the controls in Group II, a significant reported in other studies, both globally and across
difference was also observed (P < 0.0001). Interestingly, age groups, reaffirming the validity of our results .
[27]
when utilizing ANOVA, no significant difference was Furthermore, several other studies have suggested that
observed among different Dukes stages. This indicates elevated testosterone levels in CRC patients at Dukes stages
that all observed differences within the Dukes stages were B and C may be indicative of more aggressive cancers [28-30] .
negligible, as shown in Table 2. ANOVA is a justified and Increased testosterone levels have been associated with
widely accepted statistical method in scientific research cancer progression and are used as a prognostic indicator
due to its ability to handle multiple groups, control for for advanced CRC, with marker sensitivity increasing
experiment-wise error, provide valuable insights into with tumor stages [31-33] . However, it is worth noting that a
variability, and offer flexibility for various experimental population-based study involving 3635 males revealed no
designs. It helps researchers make informed decisions and correlation between testosterone levels and the incidence of
draw meaningful conclusions from their data, contributing colon cancer, which contradicts the findings of our study .
[34]
to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Pregnenolone, 17-hydroxypregnenolone, and
4. Discussion dehydroepiandrosterone are intermediates in one
of the pathways through which testosterone can be
CRC is a complex illness influenced by various risk factors, synthesized from cholesterol [5,35] . In males, the smooth
including environmental exposure to chemicals, toxins, endoplasmic reticulum of Leydig cells in the testes is
and carcinogens, as well as endogenous factors. One primarily responsible for testosterone production. In
such endogenous factor is reduced testosterone levels, females, testosterone is primarily produced by the ovaries,
which play a crucial role in controlling cell proliferation suprarenal glands, and adipose tissue. In obese individuals,
and apoptosis in healthy cells , as shown in Figure 3. As testosterone is often converted to estradiol by the enzyme
[21]
testosterone levels decrease due to various factors, such as aromatase. In addition, androstenedione and testosterone
aging, alcohol consumption, and smoking, the risk of CRC can undergo extra glandular aromatization to produce
increases. However, there is limited knowledge regarding estrone and estradiol, respectively . SHBG is a hepatically
[36]
how testosterone affects cancer cells or the potential produced glycoprotein that serves as the primary transport
inhibitory effects of anti-androgens [22,23] . Recent research protein for testosterone, playing a crucial role in regulating
has proposed testosterone as a potential tumor biomarker its bioactivity, as shown in Figure 3. Altered levels of
for CRC , alongside established tumor markers such as a SHBG also contribute to CRC risk [19,37,38] . One important
[24]
carcinoembryonic antigen. site where this regulation occurs is within the colon
In the present study, when comparing the mean epithelial cells. When the SHBG complex with testosterone
testosterone levels among CRC participants who consume reaches these cells, testosterone is released. Due to its
alcohol and smoke to those in the control group who lipophilic nature, it can easily pass through the cell
were non-smokers, non-drinkers, and control groups, membrane [12,39,40] . Once inside the cytoplasm, it binds to
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1082