Page 67 - GPD-2-3
P. 67
Gene & Protein in Disease Testosterone as a biomarker of colorectal cancer
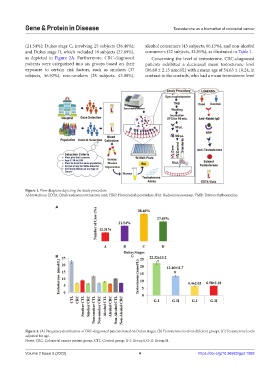
(21.54%); Dukes stage C, involving 25 subjects (38.46%); alcohol consumers (43 subjects, 66.15%), and non-alcohol
and Dukes stage D, which included 18 subjects (27.69%), consumers (22 subjects, 33.85%), as illustrated in Table 1.
as depicted in Figure 2A. Furthermore, CRC-diagnosed Concerning the level of testosterone, CRC-diagnosed
patients were categorized into six groups based on their patients exhibited a decreased mean testosterone level
exposure to certain risk factors, such as smokers (37 (06.68 ± 2.15 nmol/L) with a mean age of 54.63 ± 10.24, in
subjects, 56.92%), non-smokers (28 subjects, 43.08%), contrast to the controls, who had a mean testosterone level
Figure 1. Flow diagram depicting the study procedure.
Abbreviations: EDTA: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; HRP: Horseradish peroxidase; RIA: Radioimmunoassay; TMB: Tetramethylbenzidine.
A
B C
Figure 2. (A) Frequency distribution of CRC-diagnosed patients based on Dukes stages. (B) Testosterone levels in different groups. (C) Testosterone levels
adjusted for age.
Notes: CRC: Colorectal cancer patient group; CTL: Control group; G-I: Group I; G-II: Group II.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1082