Page 79 - GPD-2-3
P. 79
Gene & Protein in Disease Hotspots in the FOXO4: p53 interaction
FOXO4 short and FOXO4-DRI short were determined
to be 17.5 μM and 39.3 nM, respectively (Figure 2).
Interestingly, the majority of the binding in vitro is retained
when truncating the 27 L-amino acids of FOXO4-DRI
(Figure 4A) to the 9 amino acids of FOXO4-DRI_short
(Figure 2A). This observation suggests that the majority of
the interactions between the DRI peptide and p53-DBD
occur with Pocket 2 (Figures 1B and 2B) of p53-DBD.
A similar effect is observed in the K values of FOXO4
d
and FOXO4_short, where the majority of the binding
interaction is preserved upon truncation to the 9 amino
acids of FOXO4_short. This retention of binding affinity
may be attributed to the insufficient binding of FOXO4-DRI
to p53, likely due to reduced flexibility in the longer helix,
as suggested by molecular modeling (Figure 3B and C). As
depicted in Figure 3A, the conformation of bound FOXO4,
composed of L-amino acids, is predicted to consist of an
α helix and a loop, suggesting good flexibility. In contrast,
the FOXO4-DRI (Figure 3B and C), composed of D-amino
acids, retains an overall helical conformation – suggesting
a lower entropic penalty upon binding to p53 than that
displayed in its L-amino acid equivalent.
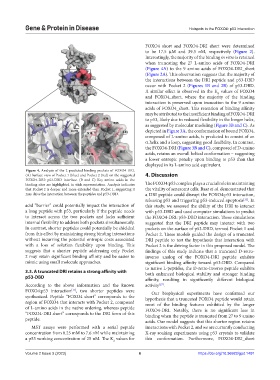
Figure 4. Analysis of the 2 predicted binding pockets of FOXO4-DRI.
(A) Surface view of Pocket 1 (blue) and Pocket 2 (red) on the suggested 4. Discussion
FOXO4-DRI: p53-DBD interface. (B and C) Key amino acids in the
binding sites are highlighted in stick representation. Analysis indicates The FOXO4:p53 complex plays a crucial role in maintaining
that Pocket 2 is deeper and more extended than Pocket 1, suggesting it the vitality of senescent cells. Baar et al. demonstrated that
may drive the interaction between the peptides and p53-DBD. a DRI peptide could disrupt the FOXO4:p53 interaction,
releasing p53 and triggering p53-induced apoptosis . In
[11]
acid “barrier” could potentially impact the interaction of this study, we assessed the ability of the DRI to interact
a long peptide with p53, particularly if the peptide needs with p53-DBD and used computer simulations to predict
to interact across the two pockets and lacks sufficient the FOXO4-DRI: p53-DBD interaction. These simulations
internal flexibility to address both pockets simultaneously. suggested that the DRI peptide may interact with two
In contrast, shorter peptides could potentially be shielded pockets on the surface of p53-DBD, termed Pocket 1 and
from this effect by maintaining strong binding interactions Pocket 2. These models guided the design of a truncated
without incurring the potential entropic costs associated DRI peptide to test the hypothesis that interaction with
with a loss of solution flexibility upon binding. This Pocket 2 is the driving factor in this proposed model. The
suggests that a shorter peptide addressing only Pocket findings of this study indicate that a truncated D-retro-
2 may retain significant binding affinity and be easier to inverso analog of the FOXO4-DRI peptide exhibits
mimic using small molecule approaches. significant binding affinity toward p53-DBD. Compared
to native L-peptides, the D-retro-inverso peptide exhibits
3.3. A truncated DRI retains a strong affinity with both enhanced biological stability and stronger binding
p53-DBD
affinity, resulting in significantly different biological
According to the above information and the known activity .
[27]
FOXO4:p53 interaction , two shorter peptides were Our biophysical experiments have confirmed our
[11]
synthesized. Peptide “FOXO4 short” corresponds to the hypothesis that a truncated FOXO4 peptide would retain
region of FOXO4 that interacts with Pocket 2, composed most of the binding features exhibited by the longer
of L-amino acids in the native ordering, whereas peptide FOXO4-DRI. Notably, there is no significant loss in
“FOXO4-DRI short” corresponds to the DRI form of this binding when the peptide is truncated from 27 to 9 amino
peptide. acids. Our model suggests that this shorter region retains
MST assays were performed with a serial peptide interactions with Pocket 2, and we are currently conducting
concentration from 0.25 mM to 7.6 nM while maintaining X-ray soaking experiments using p53 crystals to validate
a p53 working concentration of 25 nM. The K values for this conformation. Furthermore, FOXO4-DRI_short
d
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1491