Page 35 - GPD-2-4
P. 35
Gene & Protein in Disease Cyanine and cancer therapy
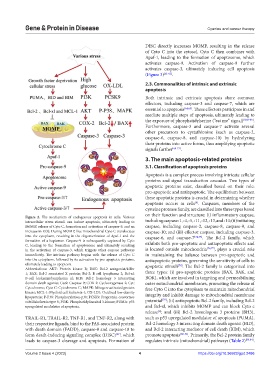
DISC directly increases MOMP, resulting in the release
of Cyto C into the cytosol. Cyto C then combines with
Apaf-1, leading to the formation of apoptosome, which
activates caspase-9. Activation of caspase-9 further
activates caspase-3, ultimately inducing cell apoptosis
(Figure 3) [61-63] .
2.3. Commonalities of intrinsic and extrinsic
apoptosis
Both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis share common
effectors, including caspase-3 and caspase-7, which are
essential to apoptosis [64,65] . These effectors participate in and
mediate multiple steps of apoptosis, ultimately leading to
the exposure of phosphatidylserine (“eat me” signal) [8,66-68] .
Furthermore, caspase-3 and caspase-7 activate several
other precursors to cystathionine (such as caspase-2,
caspase-6, caspase-8, and caspase-10) by hydrolyzing
their proteins into active forms, thus amplifying apoptotic
signals further [69-73] .
3. The main apoptosis-related proteins
3.1. Classification of apoptosis proteins
Apoptosis is a complex process involving intricate cellular
proteins and signal transduction cascades. Two types of
apoptotic proteins exist, classified based on their role:
pro-apoptotic and antiapoptotic. The equilibrium between
these apoptotic proteins is crucial in determining whether
[9]
apoptosis occurs in cells . Caspases, members of the
cysteine protease family, are classified into three types based
on their function and structure: (i) inflammatory caspase,
Figure 2. The mechanism of endogenous apoptosis in cells. Various
intracellular stress stimuli can induce apoptosis, ultimately leading to including caspase-1, -4, -5, -11, -12, -13, and -14; (ii) initiating
MOMP, release of Cyto C, formation and activation of caspase-9, and an caspase, including caspase-2, caspase-8, caspase-9, and
increase in ROS. During MOMP, free mitochondrial Cyto C translocates caspase-10; and (iii) effector caspase, including caspase-3,
into the cytoplasm, resulting in the oligomerization of Apaf-1 and the caspase-6, and caspase-7 [74,75] . The Bcl-2 family, which
formation of a heptamer. Caspase-9 is subsequently captured by Cyto
C, leading to the formation of apoptosome and ultimately resulting exhibits both pro-apoptotic and antiapoptotic effects and
in the activation of caspase-3, which triggers other caspase pathways is located outside mitochondria [76,77] , plays a crucial role
immediately. The intrinsic pathway begins with the release of Cyto C in maintaining the balance between pro-apoptotic and
into the cytoplasm, followed by its activation by pro-apoptotic proteins, antiapoptotic proteins, governing the sensitivity of cells to
ultimately leading to apoptosis. apoptotic stimuli . The Bcl-2 family is categorized into
[78]
Abbreviations: AKT: Protein kinase B; BAK: Bcl-2 antagonist/killer
1; BAX: Bcl-2 associated X protein; Bcl-2: B cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-xl: three types: (i) pro-apoptotic proteins (BAX, BAK, and
B-cell leukemia/lymphoma xl; BID: Bcl-2 homology 3 interacting BOK), which are involved in targeting and permeabilizing
domain death agonist; Cas9: Caspase-9; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; Cyt: outer mitochondrial membranes, promoting the release of
Cytochrome; Cyto C: Cytochrome C; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein free Cyto C into the cytoplasm to maintain mitochondrial
kinase; MCL-1: Myeloid cell leukemia-1; OX-LDL: Oxidized low-density integrity and inhibit damage to mitochondrial membrane
lipoprotein; P-P38: Phosphorylation-p38; PCSK9: Proprotein convertase
[79]
subtilisin/kexin type 9; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PUMA: p53 potential ; (ii) antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family, including Bcl-2
upregulated modulator of apoptosis. and Bcl-xl, which inhibits MOMP and can block Cyto c
[6]
release ; and (iii) Bcl-2 homologous 3 proteins (BH3),
TRAIL-R1, TRAIL-R2, TNF-R1, and TNF-R2, along with such as p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA),
their respective ligands, bind to the FAS-associated protein Bcl-2 homology 3 interacting domain death agonist (BID),
with death domain (FADD), caspase-8 and caspase-10 to and Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death (BIM), which
form death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) , which promote apoptosis [80-82] . Primarily, the Bcl-2 protein family
[27]
leads to caspase-3 cleavage and apoptosis. Formation of regulates intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathways (Table 2) [83,84] .
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.2486