Page 70 - GPD-2-4
P. 70
Gene & Protein in Disease Topical Me-EGF application in melanoma tumor growth
A B
C D
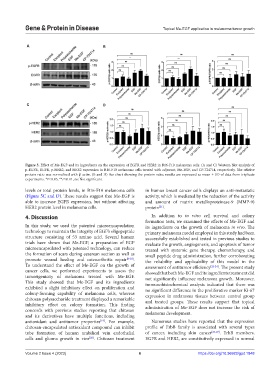
Figure 5. Effect of Me-EGF and its ingredients on the expression of EGFR and HER2 in B16-F10 melanoma cells. (A and C) Western blot analysis of
p-EGFR, EGFR, p-HER2, and HER2 expression in B16-F10 melanoma cells treated with adjuvant, Me-EGF, and CP-724714, respectively. The relative
protein ratio was normalized with β-actin. (B and D) Bar chart showing the protein ratio; results are expressed as mean ± SD of data from triplicate
experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ns: Not significant.
levels or total protein levels, in B16-F10 melanoma cells in human breast cancer cells displays an anti-metastatic
(Figure 5C and D). These results suggest that Me-EGF is activity, which is mediated by the reduction of the activity
able to increase EGFR expression, but without affecting and amount of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9)
HER2 protein level in melanoma cells. protein .
[21]
4. Discussion In addition to in vitro cell survival and colony
formation tests, we examined the effects of Me-EGF and
In this study, we used the patented microencapsulation its ingredients on the growth of melanoma in vivo. The
technology to maintain the integrity of EGF’s oligopeptide primary melanoma model employed in this study had been
structure consisting of 53 amino acid. Several human successfully established and tested in previous studies to
trials have shown that Me-EGF, a preparation of EGF evaluate the growth, angiogenesis, and apoptosis of tumor
microencapsulated with patented technology, can reduce treated with systemic gene therapy, chemotherapy, and
the formation of scars during cesarean section as well as small peptide drug administration, further corroborating
promote wound healing and osteoarthritis repair [8-10] . the reliability and applicability of this model in the
To understand the effect of Me-EGF on the growth of assessment of antitumor efficiency [22-24] . The present study
cancer cells, we performed experiments to assess the showed that both Me-EGF and its ingredients treatment did
tumorigenicity of melanoma treated with Me-EGF. not significantly influence melanoma growth. Moreover,
This study showed that Me-EGF and its ingredients immunohistochemical analysis indicated that there was
exhibited a slight inhibitory effect on proliferation and no significant difference in the proliferative marker Ki-67
colony-forming capability of melanoma cells, whereas expression in melanoma tissues between control group
chitosan polysaccharide treatment displayed a remarkable and treated groups. These results support that topical
inhibitory effect on colony formation. This finding administration of Me-EGF does not increase the risk of
concords with previous studies reporting that chitosan melanoma development.
and its derivatives have multiple functions, including
antioxidant and antitumor properties . For example, Numerous studies have reported that the expression
[19]
chitosan-encapsulated antioxidant compound can inhibit profile of ErbB family is associated with several types
tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial of cancer, including skin cancer [25-27] . ErbB members,
cells and glioma growth in vivo . Chitosan treatment EGFR and HER2, are constitutively expressed in normal
[20]
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1848