Page 71 - GPD-3-1
P. 71
Gene & Protein in Disease Hereditary angioedema
and submucosal tissues. During an AE episode, plasma diseases, leading to misdiagnosis. Furthermore,
6
12
levels of bradykinin significantly increase, reaching up to individuals may not be screened for the disease following
seven times the normal level. Unlike histamine-induced initial symptoms, especially if they do not have family
7
AE, antihistamines are ineffective when bradykinin is the members with a confirmed diagnosis of AE.
causative factor. 7,8
Detailed history taking is crucial in the evaluation
2. Case presentation of AE, encompassing inquiries about familial and drug
backgrounds. Patients with AE manifest swelling in
We report the case of a 75-year-old patient with a personal areas such as the throat, face, lips, mouth, eyes, genitalia,
history of recurring episodes of facial edema since a young and extremities. Furthermore, people with abdominal
9
age and a family history of AE in a parent and brother. AE may display symptoms such as colicky abdominal
The patient was admitted to the emergency room with pain, vomiting, and abdominal distension as a result of
generalized edema of the face, which developed over submucosal edema of the bowel wall, which can lead to
14 h without dyspnea or other associated signs. During intestinal blockage. Swelling of the uvula or tongue can
the clinical examination, we observed a eupneic patient be directly observed; however, it is advisable to perform a
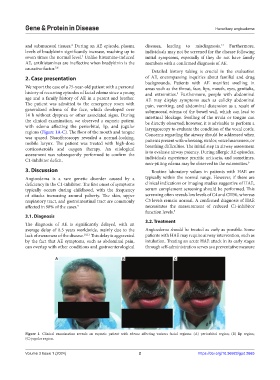
with edema affecting the periorbital, lip, and jugular laryngoscopy to evaluate the condition of the vocal cords.
regions (Figure 1A-C). The floor of the mouth and tongue Concerns regarding the airway should be addressed when
was spared. Nasofibroscopy revealed a normal-looking, patients present with wheezing, stridor, voice hoarseness, or
mobile larynx. The patient was treated with high-dose breathing difficulties. The initial step in airway assessment
corticosteroids and oxygen therapy. An etiological is to evaluate airway patency. During allergic AE episodes,
assessment was subsequently performed to confirm the individuals experience pruritic urticaria, and sometimes,
C1-inhibitor deficit.
non-pitting edema may be observed in the extremities. 9
3. Discussion Routine laboratory values in patients with HAE are
Angioedema is a rare genetic disorder caused by a typically within the normal range. However, if there are
deficiency in the C1-inhibitor. The first onset of symptoms clinical indications or imaging studies suggestive of HAE,
typically occurs during childhood, with the frequency serum complement screening should be performed. This
of attacks increasing around puberty. The skin, upper screening often reveals low levels of C4 and CH50, whereas
respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract are commonly C3 levels remain normal. A confirmed diagnosis of HAE
affected in 98% of the cases. 9 necessitates the measurement of reduced C1-inhibitor
function levels. 9
3.1. Diagnosis
3.2. Treatment
The diagnosis of AE is significantly delayed, with an
average delay of 8.5 years worldwide, mainly due to the Angioedema should be treated as early as possible. Some
lack of awareness of the disease. 10,11 This delay is aggravated patients with HAE may require airway intervention, such as
by the fact that AE symptoms, such as abdominal pain, intubation. Treating an acute HAE attack in its early stages
can overlap with other conditions and gastroenterological through self-administration serves as a preventative measure
A B C
Figure 1. Clinical examination reveals an eupneic patient with edema affecting various facial regions: (A) periorbital region; (B) lip region;
(C) jugular region.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.2665