Page 109 - GPD-3-2
P. 109
Gene & Protein in Disease Inhibition of SOD1 in diseases
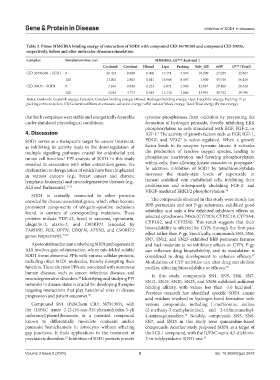
Table 3. Prime MMGBSA binding energy of interaction of SOD1 with compound CID 36791369 and compound CID 30935,
respectively, before and after molecular dynamics simulation
Complex Simulation time (ns) MMGBSA ΔG bind (kcal·mol )
‑1
Coulomb Covalent Hbond Lipo Packing Solv_GB vdW G bind (Total)
CID 36791369 – SOD1 0 26.424 8.668 −0.000 −17.151 −5.576 −18.209 −27.025 −32.867
100 13.001 2.805 −0.611 −15.064 −8.597 −1.900 −45.746 −56.110
CID 30935 – SOD1 0 −3.166 0.816 −1.223 −6.874 −1.900 12.937 −29.108 −28.518
100 −4.042 4.773 −1.955 −11.130 −1.686 13.991 −39.742 −39.790
Notes: Coulomb: Coulomb energy; Covalent: Covalent binding energy; Hbond: Hydrogen bonding energy; Lipo: Lipophilic energy; Packing: Pi-pi
packing correction; Solv GB: Generalized Born electrostatic solvation energy; vdW: van der Waals energy; Total: Total energy (Prime energy).
that both complexes were stable and energetically favorable tyrosine phosphatases from oxidation by preventing the
under simulated physiological conditions. formation of hydrogen peroxide, thereby inhibiting ERK
phosphorylation in cells stimulated with EGF, FGF-2, or
4. Discussion IGF-1. The activity of growth factors such as EGF, IGF-1,
2
SOD1 serves as a therapeutic target for cancer treatment, PDGF, and VEGF is redox-regulated. When a growth
as inhibiting its activity leads to the downregulation of factor binds to its receptor tyrosine kinase, it activates
multiple signaling pathways crucial for endothelial and the production of reactive oxygen species, leading to
tumor cell function. PPI analysis of SOD1 in this study phosphatase inactivation and favoring phosphorylation
2
2
revealed its association with other antioxidant genes, the within cells, thus allowing kinase cascades to propagate.
dysfunction or deregulation of which have been implicated In addition, inhibition of SOD1 by tetrathiomolybdate
in various cancers (e.g., breast cancer and chronic increases the steady-state levels of superoxide in
lymphatic leukemia) and neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., human umbilical vein endothelial cells, inhibiting their
ALS and Parkinson’s). 27-31 proliferation and subsequently abolishing FGF-2- and
VEGF-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation. 36
SOD1 is centrally connected to other proteins
encoded by disease-associated genes, which often become The compounds obtained in this study were mostly not
prominent components of ubiquitin-positive inclusions BBB permeants and not P-gp substrates, exhibited good
found in carriers of corresponding mutations. These solubility, and only a few exhibited inhibitory effects on
proteins include TDP-43, fused in sarcoma, optineurin, selected cytochrome P450s (CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4,
ubiquilin-2, ataxin-2, and C9ORF72 (encoded by CYP1A2, and CYP2D6). This result suggests that their
TARDBP, FUS, OPTN, UBQLN, ATXN2, and C9ORF72 bioavailability is affected by CYPs through the first-pass
genes, respectively). 31,32 effect rather than P-gp. Specifically, compounds SN5, SN6,
SN7, SN12, and SN25 exhibited BBB permeant features
A potential mechanism underlying SOD1 pathogenesis in and had moderate to no inhibitory effects on CYPs. P-gp
ALS involves gain-of-interaction, where mis-folded soluble can influence drug bioavailability, and its modulation is
SOD1 forms abnormal PPIs with various cellular proteins, considered in drug development to enhance efficacy.
37
including other SOD1 molecules, thereby disrupting their Modulation of CYP activities can alter drug metabolism
function. These aberrant PPIs are associated with numerous profiles, affecting bioavailability or efficacy. 38
human diseases, such as cancer, infectious diseases, and In this study, compounds SN1, SN5, SN6, SN7,
neurodegenerative disorders. Identifying and studying PPI SN12, SN19, SN20, SN25, and SN36 exhibited sufficient
33
networks in disease states is crucial for developing therapies binding affinity, with values less than -5.0 kcal·mol .
-1
targeting interactions that play functional roles in disease Previous research has identified specific SOD1 amino
progression and patient outcomes. 34
acid residues involved in hydrogen bond formation with
Compound SN1 (PubChem CID: 36791369), with various compounds, including L-methionine, aniline
the IUPAC name 2-[2-[(6-oxo-5H-phenanthridin-3-yl) (2-methoxy-5-methylaninline), and 2-trifluoromethyl-
carbamoyl]phenyl]benzoate, is a patented compound 4-aminoquinazoline. Notably, compounds SN5, SN6,
39
known to differentially modulate connexin and/or SN7, and SN25 in this study were quinazoline-based
pannexin hemichannels in astrocytes without affecting compounds. Another study proposed SOD1 as a target of
gap junctions. It finds applications in the treatment of the LCS-1 compound, with the IUPAC name 4,5-dichloro-
psychiatric disorders. Inhibition of SOD1 protects protein 2-m-tolylpyridazin-3(2H)-one. 13
35
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/gpd.3042