Page 25 - GPD-3-2
P. 25
Gene & Protein in Disease Review of CAR-T in ADs
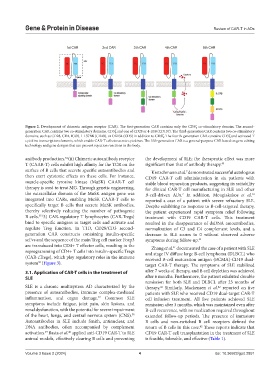
Figure 2. Development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). The first-generation CAR contains only the CD3ζ co-stimulatory domain. The second-
generation CAR contains two co-stimulatory domains, CD3ζ and one of CD28 or 4-1BB (CD137). The third-generation CAR contains two co-stimulatory
domains, such as CD28, CD4, ICOS, 1-137BB (CD40), or OX134 (CD3) in addition to CD3ζ. The fourth-generation CAR contains CD3ζ and activated T
cytokine transcription elements, which enable CAR-T cells to secrete cytokines. The fifth-generation CAR is a general-purpose CAR based on gene editing
technology and gene designs that can prevent rejection reactions in the body.
34
antibody production. (ii) Chimeric autoantibody receptor the development of SLE; the therapeutic effect was more
T (CAAR-T) cells exhibit high affinity for the TCR on the significant than that of antibody therapy. 40
surface of B cells that secrete specific autoantibodies and Kretschmann et al. demonstrated successful autologous
7
then exert cytotoxic effects on these cells. For instance, CD19 CAR-T cell administration in six patients with
muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) CAAR-T cell stable blood separation products, suggesting its suitability
therapy is used to treat MG. Through genetic engineering, for clinical CAR-T cell manufacturing in SLE and other
the extracellular domain of the MuSK antigen gene was B-cell-driven ADs. In addition, Mougiakakos et al.
7
34
integrated into CARs, enabling MuSK CAAR-T cells to reported a case of a patient with severe refractory SLE.
specifically target B cells that secrete MuSK antibodies, Despite exhibiting no response to B-cell-targeted therapy,
thereby selectively reducing the number of pathogenic the patient experienced rapid symptom relief following
B cells. 3) CAR-regulatory T lymphocytes (CAR-Tregs) treatment with CD19 CAR-T cells. This treatment
35 (
bind to specific antigens in target cells and activate and resulted in the disappearance of dsDNA autoantibodies,
regulate Treg function. In T1D, CD28/CD3 second- normalization of C3 and C4 complement levels, and a
generation CAR constructs containing insulin-specific decrease in SLE scores to 0 without observed adverse
scFvs and the sequence of the main Treg cell marker Foxp3 symptoms during follow-up. 34
are transduced into CD4+ T effector cells, resulting in the Zhang et al. documented the case of a patient with SLE
41
reprogramming of CD4+ T cells into insulin-specific Tregs and stage IV diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who
(CAR-cTregs), which play regulatory roles in the immune received B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-CD19 dual-
system (Figure 3). target CAR-T therapy. The symptoms of SLE stabilized
36
3.1. Application of CAR-T cells in the treatment of after 7 weeks of therapy, and B cell depletion was achieved
SLE after 6 months. Furthermore, the patient exhibited durable
remission for both SLE and DLBCL after 23 months of
SLE is a chronic multisystem AD characterized by the therapy. Similarly, Mackensen et al. reported on five
41
42
presence of autoantibodies, immune complex-mediated patients with SLE who received CD19 dual-target CAR-T
inflammation, and organ damage. Common SLE cell infusion treatment. All five patients achieved SLE
37
symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin lesions, and remission after 3 months, which was maintained even after
renal dysfunction, with the potential for severe impairment B-cell recurrence, with no medication required throughout
of the heart, lungs, and central nervous system (CNS). extended follow-up periods. The presence of immature
38
Autoantibodies in SLE include Smith, antinuclear, and B cells and non-switched B cell receptors defined the
DNA antibodies, often accompanied by complement return of B cells in this case. These reports indicate that
42
activation. Basta et al. applied anti-CD19 CAR-T to SLE CD19 CAR-T cell transplantation in the treatment of SLE
39
40
animal models, effectively clearing B cells and preventing is feasible, tolerable, and effective (Table 1).
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2851