Page 24 - GPD-3-2
P. 24
Gene & Protein in Disease Review of CAR-T in ADs
antigen with high affinity and is used to stimulate CAR improving their proliferation and persistence. Fourth-
signaling and T-cell activation. Hinges derived from generation CARs, compared with third-generation CARs,
25
CD8, CD28, IgG1, or IgG4 are flexible segments that integrate an activated T cell-nuclear factor transcription
overcome spatial hindrance, allowing CAR to transmit response element. After CAR-T cells recognize target
signals and recognize T cell activation. Transmembrane antigens, they activate downstream transcription factors
26
domains from CD3ζ, CD28, CD4, and CD8α not only and stimulate the production of cytokines, which improve
serve to anchor the antigen-binding domain to the cell T cell survival rates and recruit and activate other immune
membrane but also play a crucial role in the activity of cells. Fifth-generation CARs are created by combining
CAR. The intracellular co-stimulatory domain includes an IL-2 receptor chain fragment (IL-2R) with a second-
27
the activation and co-stimulatory domains, and common generation CAR. The JAK-STAT signaling pathway
co-stimulatory domains include CD28 and 4-1BB is activated by the downstream signaling pathway of
(CD137) (Figure 1). 28,29 IL-2R. Furthermore, when CAR-T cells detect antigens,
the antigen-specific activation of receptors activates all
2.2. Development of CAR downstream signaling pathways, resulting in full T cell
31
To enhance the antitumor efficacy of CAR-T cells while activation and increased therapeutic agent persistence.
mitigating T-cell activation-associated cytotoxicity, CAR Fifth-generation CARs are also classified as universal CARs
technology targeting intracellular signaling pathways (UCARs), as their fabrication is based on gene editing
has been developed. The activation of T cells requires technology to prevent human rejection. They can also be
two signaling pathways. First, the TCR-CD3 complex pre-prepared for allogeneic T cells before administration
recognizes the MHC/antigenic peptide complex and but may still face clearance due to immune rejection
32
transmits the specific recognition signal. Second, non- and may induce graft-versus-host disease. Third- and
specific co-stimulatory signals are provided by APC fourth-generation CAR-T cells exhibit increased tumor-
co-stimulatory molecules. The first generation of CAR killing capacities and cytotoxicity but are presently in
contained solely the CD3ζ intracellular domain, limiting the research and development stage. Second-generation
CAR-T cell activation and proliferation in vivo. Second- CARs, characterized by their milder approach, are widely
generation CARs feature two co-stimulatory domains, employed in tumor therapy, representing the majority of
33
CD3ζ, along with either CD28 or 4-1BB (CD137), listed CAR-T products (Figure 2).
enhancing stimulation signals. These dual co-stimulatory
domains enable the CAR-T cells to proliferate extensively 3. Research progress of CAR-T in ADs
and sufficiently produce cytokines. The increased The use of CAR-T cell therapy for ADs primarily involves
expression of anti-apoptotic factors leads to the CAR-T three different mechanisms: (i) CAR-T cells recognize
cells exhibiting a longer survival time and a more durable specific antigens in target cells and initiate cytotoxic
therapeutic effect. Third-generation CARs, in addition to activity against those cells. For example, CAR-T cell
30
CD3ζ, have two co-stimulatory domains, such as CD28, therapy targeting B cell CD19 is used in the treatment of
CD4, ICOS, 1-137BB (CD40), or OX134 (CD3), which SLE. After infusion into the body of the patient, the CD19
provide T cells with more effective anti-tumor effects CAR-T cells undergo expansion and specifically target
while increasing their cytokine production ability and and eliminate CD19-expressing B cells, thereby reducing
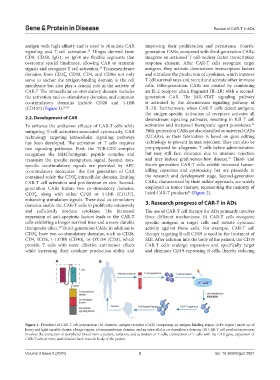
A B
Figure 1. Flowchart of CAR T cell preparation (A) chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) comprising an antigen-binding region (scFv region) made up of
heavy and light variable chains, a hinge region, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular co-stimulatory domain. (B) CAR-T cell production process
involves the extraction of peripheral blood from a patient, isolation, and activation of T cells, transfection of T cells with the CAR gene, expansion of
CAR-T cells in vitro, and infusion back into the body of the patient.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2851